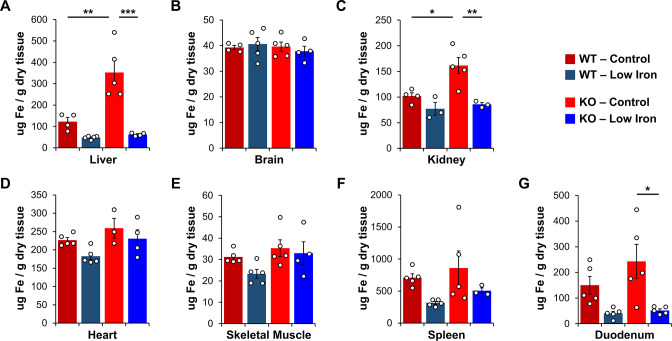
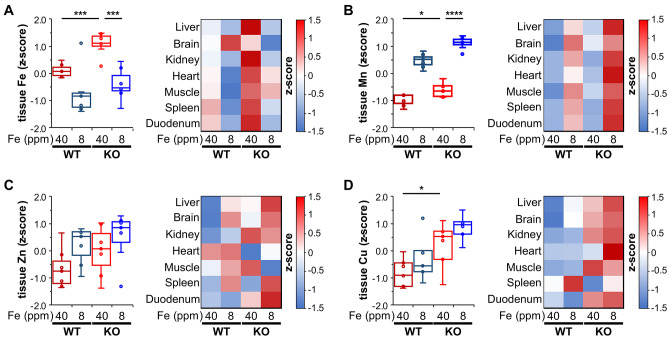
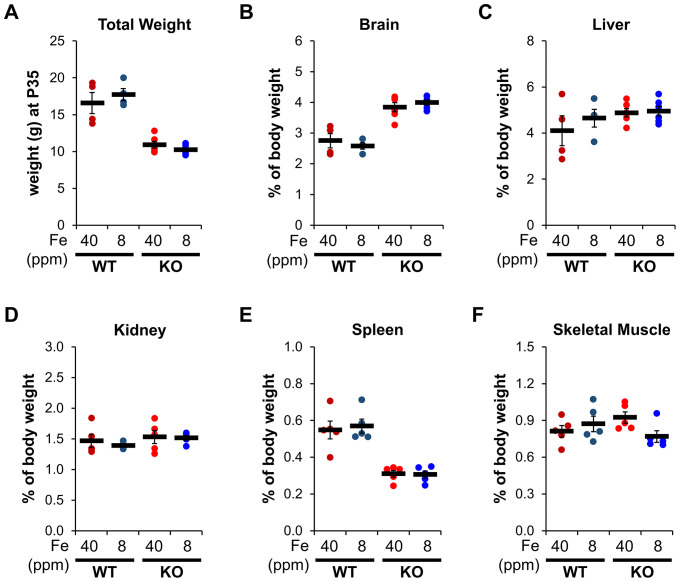
Figure 2. Total iron quantification in tissues.
Quantification of total iron by ICP-MS from WT and Ndufs4−/− mice at PND35 fed control (40 ppm) or low (8 ppm) AIN-93G in (A) liver, (B) whole brain, (C) kidney, (D) heart, (E) quadricep, (F) spleen, and (G) duodenum. N=3–5 mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ANOVA with post hoc Tukey. ICP-MS, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry; WT, wild-type.