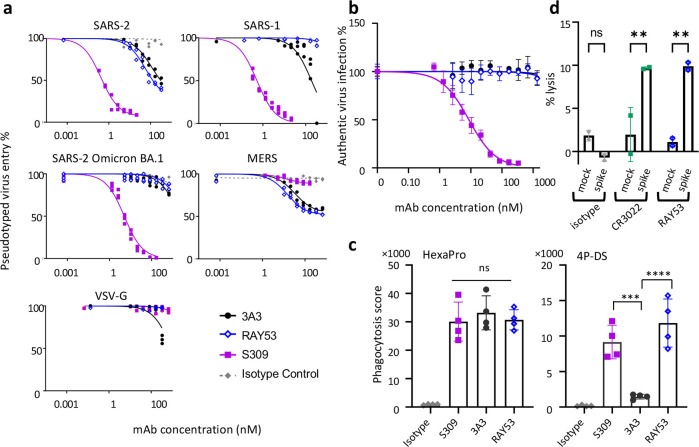
Figure 5. Targeting the hinge epitope recruits Fc effector functions.
(a) Neutralization was evaluated by pre-incubating antibody with pseudotyped HIV particles that were then added to HEK 293T cells stably expressing ACE2 (SARS-1 and SARS-2 pseudoviruses) or DPP4 (MERS pseudovirus), with viral entry detected by luciferase luminescence. The entry efficiency of pseudoviruses without any treatment was considered 100%. (b) Neutralization of authentic SARS-2 wild-type virus was assessed by incubating viral particles with antibody before adding to Vero HF cells. Viral infection was assessed by ELISPOT 24 hr after infection by immunostaining with the anti-SARS-2 nucleocapsid antibody 1C7C7. (c) ADCP was performed by co-incubating undifferentiated THP-1 cells, antibodies and pHrodo-Green/APC-polystyrene beads coated with HexaPro or 4P-DS. The phagocytosis score was calculated as the percent of positive APC/FITC cells multiplied by the GMFI for APC. Data were collected from two separate experiments with the average and standard deviation shown. (d) ADCC was assessed by incubating NK-92 V/V cells, HEK-293T cells transfected to express either wild-type SARS-2 spike (spike) or nothing (mock) and antibody. For each panel, data shown are representative of three biological replicates. Duplicate technical replicates with the midpoint of each condition are shown.