Figure 1.
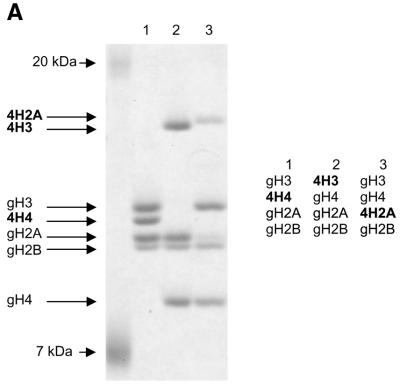
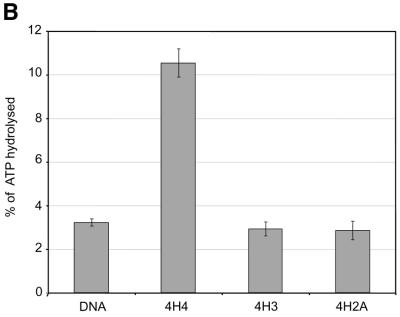
Grafting the histone H4 N-terminus on H3 and H2A prevents substrate recognition by ISWI. (A) Analysis of chimeric histone octamers. Histone octamers were refolded from sets of variant histones as indicated on the right. The globular portions of the histones (39) are indicated with the prefix ‘g’. gH3, histone H3 from K27 to A135; gH4, histone H4 from K20 to G102; gH2A, histone H2A from K13 to K118; and gH2B, histone H2B from K27 to K125. Those histones to which the H4 N-terminus was added (see Materials and Methods) are indicated with the prefix 4. Histones were analyzed by SDS–PAGE in an 18% gel and stained with Coomassie Blue. The migration of the histones and markers are indicated on the left. (B) ATPase assays with variant histone octamers. The histones shown in (A) were reconstituted into nucleosomes by NAP-1 assisted assembly in the presence of ISWI. A control reaction contained only DNA in the absence of histones. The ATPase activity of ISWI during the reaction is displayed as the percentage of ATP hydrolyzed during the assay. The bars represent the average of three independent experiments, and the variability is indicated by the error bars.