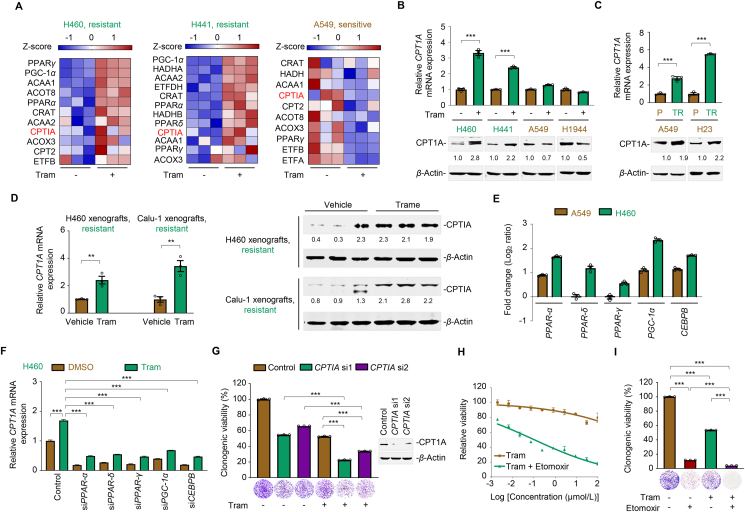
Figure 6.
CPTIA transactivation confers MEKi resistance. (A) Heat map illustrating expression of fatty acid oxidation (FAO)-associated gene signature in H460, H441, and A549. Cells were treated with trametinib at their respective 1/2 IC50 values for 24 h. Total mRNA was isolated from treated cells and sequenced. Z-scores were calculated based on counts of exon model per million mapped reads. FAO-related genes were identified by a cutoff of P < 0.05, n = 3. (B) Effects of trametinib on CPTIA mRNA (up) and protein (down) expression levels in KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells. Cells were treated with trametinib at their respective 1/2 IC50 values for 24 h. CPTIA expression was detected by RT-qPCR and immunoblot assays. MEKi-resistant cell lines are marked in green, and MEKi-sensitive cell lines are marked in brown. Data represent the mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, by unpaired, two-sided Student's t test. (C) CPTIA mRNA (up) and protein (down) expression levels in acquired resistant cell pairs (A549/P and A549/TR; H23/P and H23/TR). Data represent the mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, by unpaired, two-sided Student's t test. (D) Trametinib upregulated CPTIA expression in H460 and Calu-1 xenograft tumors. Tumors were isolated after 1-week trametinib treatment. RT-qPCR and immunoblot analysis assays were detected. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three independent biologically samples. ∗∗P < 0.01, by unpaired, two-sided Student's t test. (E) Log2 ratio values of fold change for PPARα, PPARδ, PPARγ, PGC-1α, and CEBPB transcripts in A549 and H460 cells before and after trametinib treatment. Cells were exposed to trametinib at their respective 1/2 IC50 values for 24 h. RT-qPCR analysis was further carried out. (F) CPTIA mRNA expression levels. H460 cells were treated with trametinib for 24 h after PPARs, PGC-1α, or CEBPB genetical silencing. Data represent the mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple-comparisons test. (G) CPTIA silencing enhanced the killing effects of trametinib in H460 cells. Left panel, relative viability of the culture colonies; right panel, CPTIA knockdown efficiency in H460 cells by immunoblot analysis. Data represent the mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple-comparisons test. (H, I) CPTIA inhibition by etomoxir increased the sensitivity of H460 cells to trametinib, as shown by the growth curves (H) and relative clonogenic viability (I). Data represent the mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple-comparisons test.