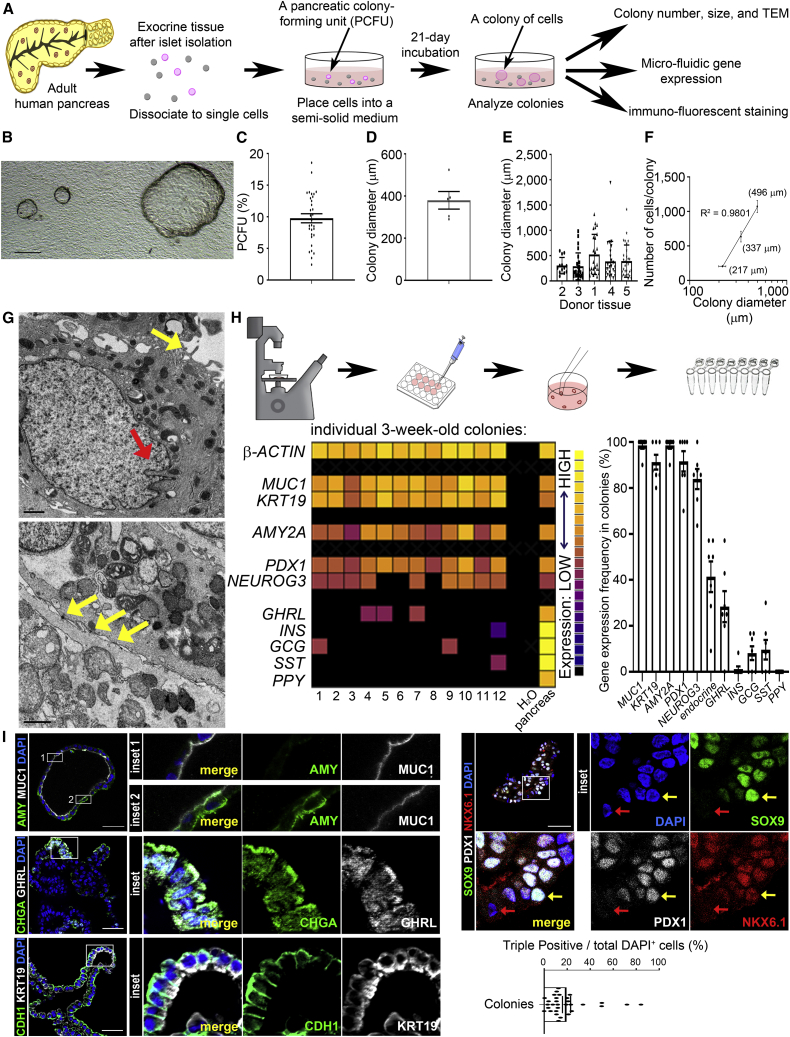
Figure 1.
Methylcellulose-based colony assay for adult human pancreatic progenitor cells capable of tri-lineage differentiation
(A) Experimental diagram.
(B) Representative bright-field image of colonies. Scale bar, 200 μm.
(C) % PCFUs in dissociated exocrine tissues is 9.8% ± 0.7% (N = 31 donors).
(D) Colony diameter = 394 ± 37 μm; mean ± SEM, ≥10 colonies per donor, N = 6 donors with 4 technical replicates.
(E) Diameters of colonies between different donors (N = 5).
(F) Mean diameter of colonies is positively correlated with the total number of cells per colony (R2 = 0.9801); mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments and 20 individual colonies per data point.
(G) TEM of 3-wo colonies displaying microvilli on the apical side (top, yellow arrow), nuclear invaginations (top, red arrow), and desmosomes (bottom, yellow arrows). Scale bars, 1 μm.
(H) Micro-manipulation of individual colony for microfluidic qRT-PCR. Representative heatmap of lineage markers; n = 58 colonies, N = 7 donors. Gene expression frequency; mean ± SD.
(I) IF staining confirms protein expression. Scale bar, 50 μm (insets enlarged 4×). Yellow arrow points to a representative cell that is triple-positive (TP) for SOX9, PDX1, and NKX6.1 and a red arrow for a non-TP cell. TP quantification represents mean ± SEM (19.5% ± 3.5%) from a total of 31 colonies from N = 3 donors. See also Figure S1B.