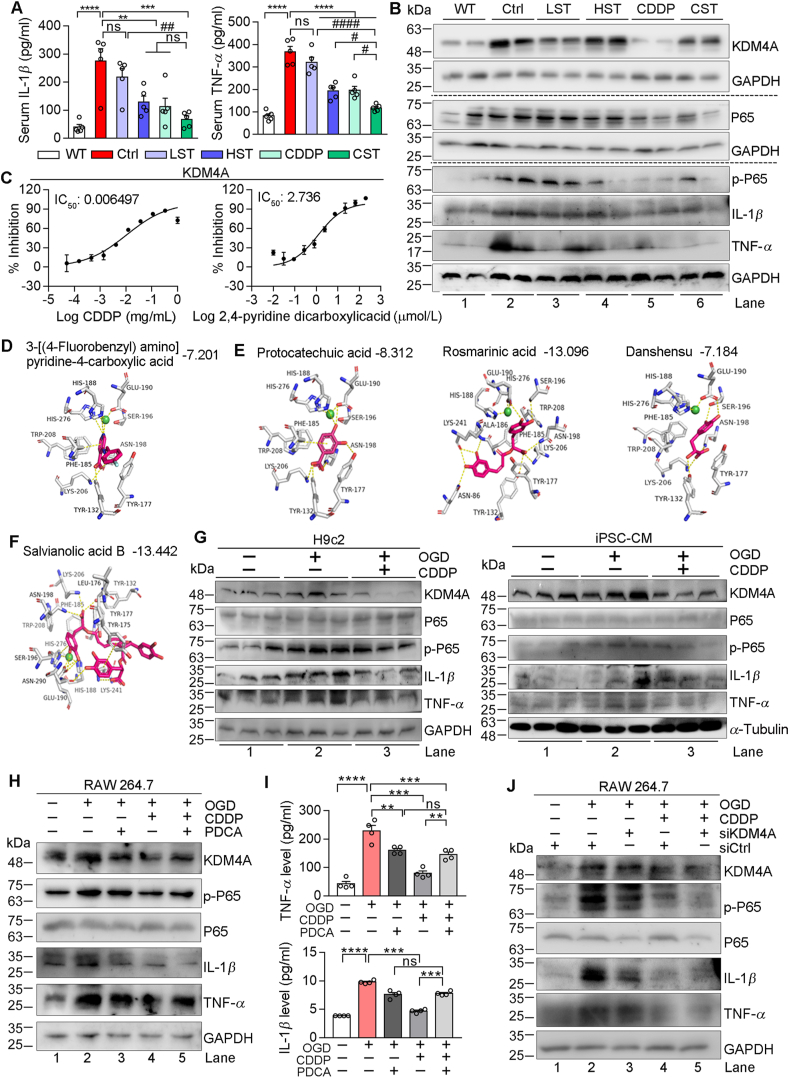
Figure 4.
CDDP inhibits KDM4A to decrease inflammation. The levels of serum TNF-α and IL-1β (A) and protein expressions of KDM4A, P65, p-P65, IL-1β and TNF-α in heart samples (B) of mice in Fig. 1 were determined by assay kits (n = 5) and Western blot, respectively. (C) Inhibition of KDM4A activity by CDDP was determined by the in vitro enzymatic activity assay system. (D–F) Molecular docking of KDM4A with the co-crystal ligand (D) or CDDP components (E, F) with the corresponding docking score shown on the top of each figure. (G–J) H9c2, iPSC-CM or RAW 264.7 cells were cultured in normal culture condition, OGD condition or OGD condition plus treatment of CDDP (G) 500 μg/mL in H9c2, 1000 μg/mL in iPSC-CM), PDCA (1 μmol/L) or CDDP plus PDCA (1 μmol/L) (H, I) for 12 h. RAW 264.7 cells in normal culture condition or OGD condition were transfected with control siRNA (siCtrl) or siRNA against KDM4A (siKDM4A), followed by CDDP treatment (J) for 12 h. After treatment, cells (G, H, J) and treatment medium (H) were collected and used to conduct the following assays: expressions of KDM4A, P65, p-P65, IL-1β and TNF-α protein were determined by Western blot, and levels of TNF-α, IL-1β in cell treatment medium were determined by ELISA assay kits. The data are shown as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01; ns: not significantly different between indicted groups.