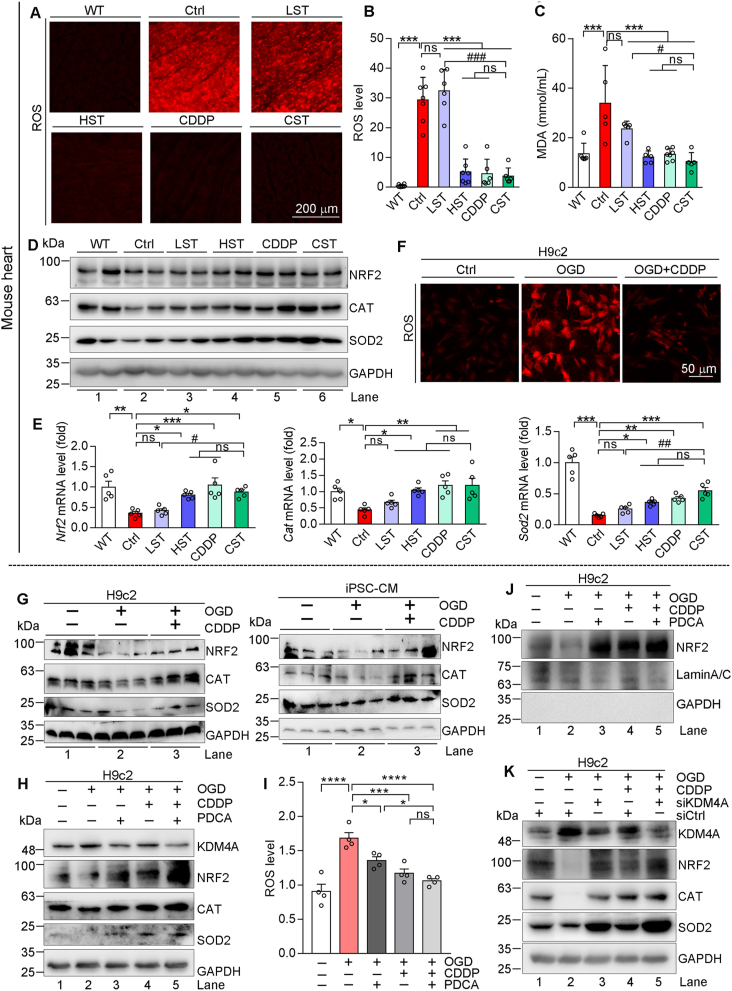
Figure 5.
CDDP inhibits KDM4A to reduce oxidative stress. (A–E) Mouse heart samples in Fig. 1 were completed the following assays. ROS levels were determined by DHE staining of heart sections, and the images were photographed by a fluorescence microscope with quantification analysis of the fluorescent intensity (A, B, n = 6). MDA levels were determined by assay kit (C, n = 5). Protein expressions of NRF2, SOD2, CAT were determined by Western blot (D). Expression of Nrf2, Sod2, Cat mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR (E, n = 5). (F–K) H9c2 or iPSC-CM cells in OGD condition received the following treatment for 12 h, and the cells in normal culture condition were used as control: CDDP at 500 or 1000 μg/mL for H9c2 or iPSC-CM cells (F, G); CDDP at 500 μg/mL and/or PDCA at 1 μmol/L (H–J); cells were transfected with siCtrl or siKDM4A as indicated, followed by CDDP (500 μg/mL) treatment (K). After treatment, cells were used to complete the following assays: cellular ROS levels by DHE staining (F) or ROS assay kit (I); expression NRF2, CAT, SOD2 and KDM4A in whole cellular extract (G, H, K) or NRF2 expression in nuclear extract (J) was determined by Western blot. The data are shown as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001; ns: not significantly different between indicated groups. MDA, malondialdehyde; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DHE, dihydroethidium.