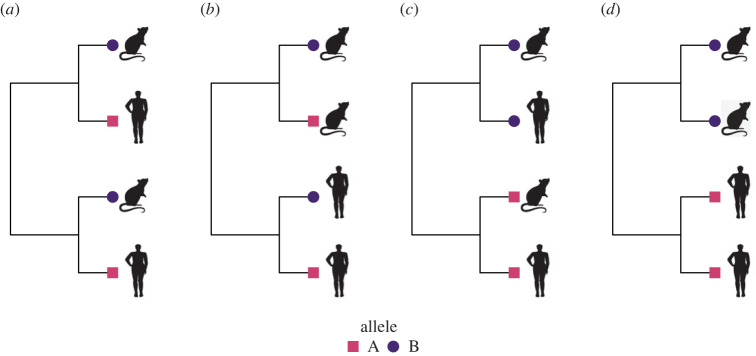
Figure 1.
(a) Viral samples were collected evenly over the phylogeny, and genetic divergence was low. The frequency of alleles would be expected to be similar in human- and rodent-derived samples. If the allele frequency at a given locus deviated from that expectation, it would indicate a species association. (b) Viral hosts were sampled unevenly, which is expected to introduce population stratification, but the severity would be tempered by the low genetic divergence. (c) Genetic divergence was high, but the samples were collected evenly across the phylogeny. The distribution of alleles would be similar in human and rodent samples. (d) Samples were collected unevenly in a genetically divergent population, producing severe population stratification.