Figure 1.
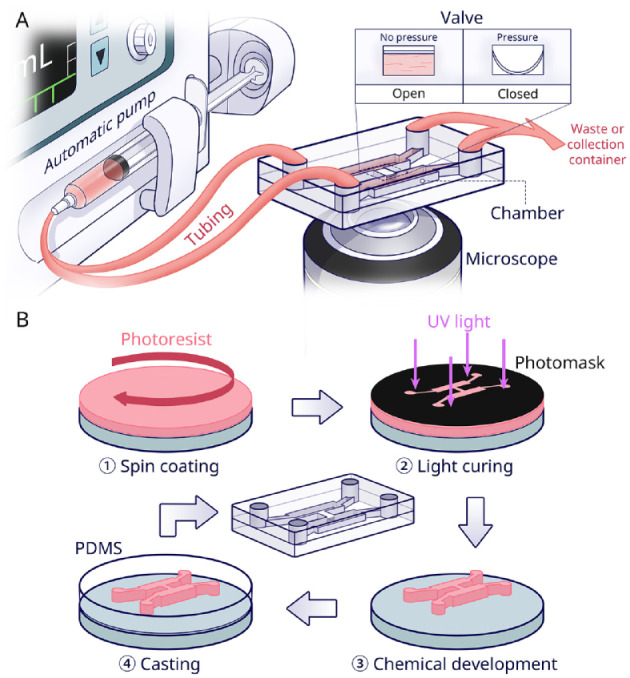
Overview of microfluidic chip technology. (A) Schematic of an automated microfluidic chip with monitoring microscope. The basic chip components include an inlet and outlet, cell culture chamber, and media transportation channel. A pump and valve are used for fluidic control in the chip. The valve is usually controlled by pressure. (B) Fabrication flow of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chip (adapted from Scott and Ali 2021). The so-called soft lithography production method, first, a photoresist material (pink), is spin-coated on a (usually silicon) substrate (gray). By UV irradiation through a photomask (black), the desired pattern is transferred onto the photoresist-coated substrate. The exposed part is subsequently cured and the non-cross-linked resist is removed. Thus, a master mold is fabricated. From the mold, PDMS casting leads to the correct microfluidic architecture. Finally, after sealing the channels and chambers by a cover, the PDMS chip is completed.
