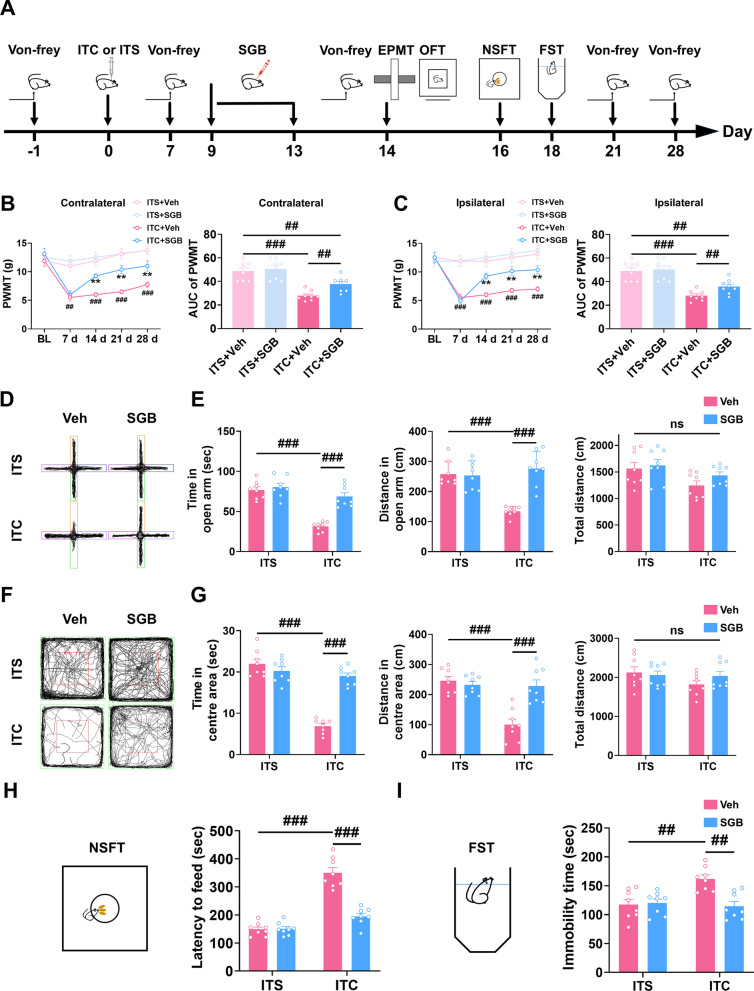
Fig. 7.
Post-treatment with repetitive SGB reversed the development of mechanical allodynia and anxiodepressive-like behaviors in CPSP rats. A The experimental timeline of surgical procedure and behavior tests. B Temporal changes of PWMT in contralateral hindpaw after thalamic hemorrhagic stroke and the area under curve of the contralateral hindpaw PWMT (n = 8, PWMT: group, F3,28 = 14.78, day, F4,112 = 29.22, group × day, F12,112 = 7.669, **p < 0.01 vs ITC + Veh, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITS + Veh; AUC: F3,28 = 18.74, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001). C Temporal changes of PWMT in ipsilateral hindpaw after thalamic hemorrhagic stroke and the area under curve of the ipsilateral hindpaw PWMT (n = 8, PWMT: group, F3,28 = 15.01, day, F4,122 = 26.73, group × day, F12,112 = 9.919, **p < 0.01 vs ITC + Veh, ###p < 0.001 vs ITS + Veh; AUC: F2,21 = 19.21, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001). D Representative track plot in the EPMT. E Repetitive SGB increased the time spent and traveled distance in the open arm in ITC group, but had no effect on ITS group (n = 8, time in open arm; F3,28 = 32.45, ###p < 0.001; distance in open arm; W3.0,13.63 = 38.47, ###p < 0.001, total distance: ns, no significance). F Representative track plot in the OFT. G Repetitive SGB increased the time spent and traveled distance in the central area in ITC group, but had no effect on ITS group (n = 8, time in central area: F3,28 = 58.17, ###p < 0.001; distance in central F3,28 = 17.36, ###p < 0.001; total distance: ns, no significance). H Repetitive SGB decreased the latency to feed in the NSFT in ITC group, but had no effect on ITS group (n = 8, F3,28 = 60.17, ###p < 0.001). I Repetitive SGB decreased the immobility time in the FST in ITC group, but had no effect on ITS group (n = 8, F3,28 = 8.058, ##p < 0.01). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, one-way or two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test, Welch ANOVA followed by Tamhane’s T2 test