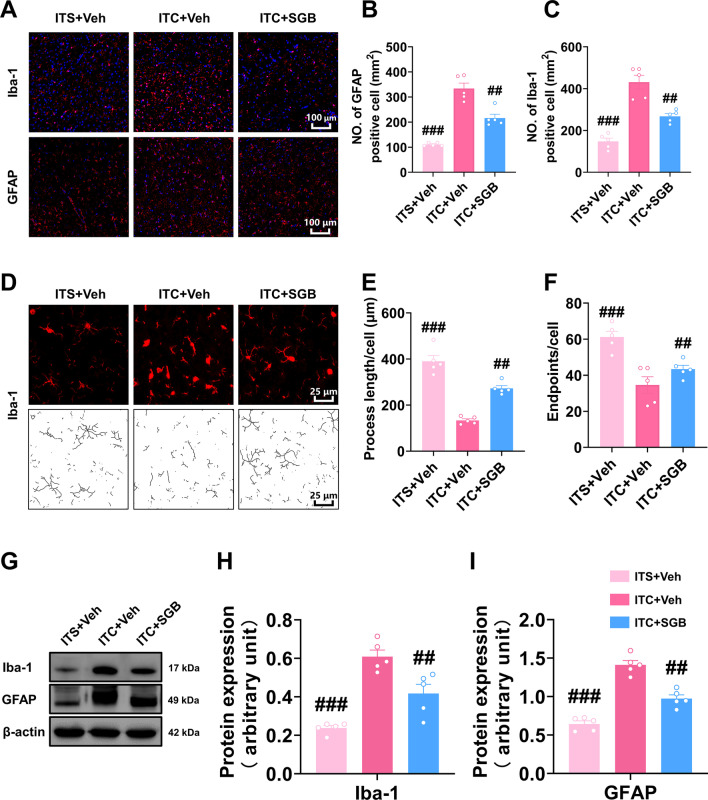
Fig. 9.
Post-treatment with repetitive SGB inhibited the activation of microglia and astrocytes in peri-thalamic lesion sites of CPSP rats. A Representative immunofluorescence images showing the expressions of GFAP and Iba-1 in the peri-thalamic lesion sites. Scale bar = 100 μm. B, C Quantification of cell number showed repetitive SGB decreased the total number of GFAP (B) and Iba-1 (C) positive cells in the peri-thalamic lesion sites of CPSP rats (n = 5, Iba-1 F2,12 = 40.67, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh; GFAP F2,12 = 99.46, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh). D Representative magnified images of microglia (top) and the corresponding black-and-white, skeletonized images (bottom) in the peri-thalamic lesion sites. Scale bar = 25 μm. E Quantification of process length showed repetitive SGB increased process length of microglia in the peri-thalamic lesion sites of CPSP rats (n = 5, F2,12 = 59.03, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh). F Quantification of endpoint showed repetitive SGB increased endpoint of microglia in the peri-thalamic lesion sites of CPSP rats (n = 5, F2,12 = 15.62, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh). g Representative western blots of Iba-1 and GFAP expression in total proteins of the peri-thalamic lesion sites, H, I Quantitative summary result showed repetitive SGB decreased Iba-1 (H) and GFAP (I) expression in the peri-thalamic lesion sites of CPSP rats (n = 5, Iba-1: F2,12 = 28.08, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh; GFAP; F2,12 = 62.45, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs ITC + Veh). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey test