FIGURE 1.
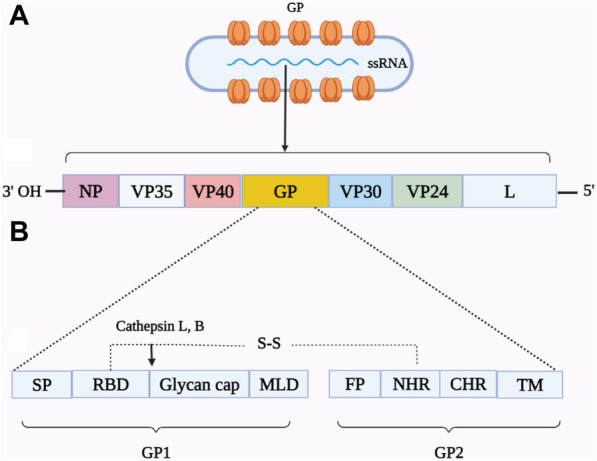
Schematic representation of the genome organization of Ebolavirus (EBOV) (A) and a linear view of the glycoprotein (GP) (B). The single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) genome of EBOV is comprised of certain encoding protein genes. The viral proteins (VP), including NP (nucleoprotein) and VP24 (matrix protein), form the ribonucleoprotein complex. Other VP, such as VP40 (matrix protein), VP30 (transcriptional factor), VP35 (polymerase cofactor), and L (RNA polymerase), are involved in the structure of the virus or replication. The surface spikes on the virion are composed of a trimeric transmembrane GP that is comprised of GP1 and GP2 linked by a disulfide bond. The GP1 subunit consists of a signal peptide (SP), a receptor-binding domain (RBD), a glycan cap, and a mucin-like domain (MLD). The GP2 subunit contains a transmembrane domain (TM) anchor to two heptad repeats, namely, N-terminal (NHR) and C-terminal (CHR) heptad repeats, and a membrane-proximal external region (not shown).
