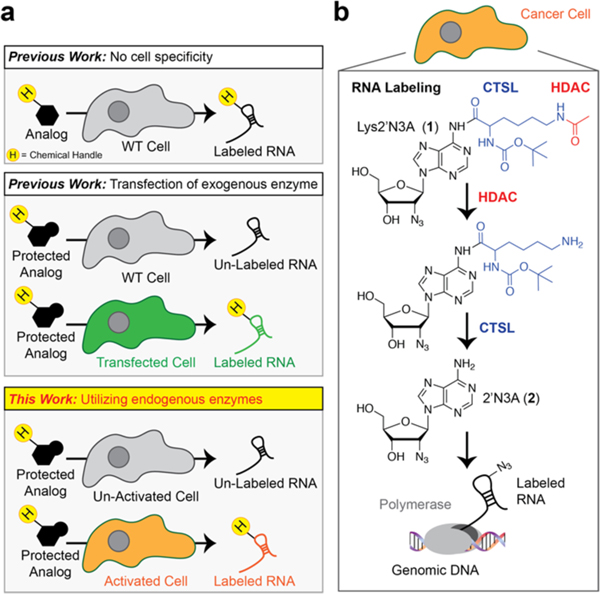
Figure 1.
Outline of cell-type specific metabolic labeling of RNA. (a) In metabolic labeling experiments, a chemically modified nucleoside analog is added to cells. The chemical modifications on the nucleobase/nucleoside analogs render them “inert” to endogenous metabolic pathways while the expression of specific metabolic enzymes can control their incorporation. Most studies to date rely on the overexpression of exogenous enzymes to control metabolic incorporation. (b) Our approach uses endogenous enzymes to “uncage” inert intermediates for eventual incorporation into RNA to apply cell-specific metabolic labeling of RNA in cancer cells. H = handle for conjugation such as alkyne or azide. HDAC = histone deacetylase. CTSL = cathepsin L protease.