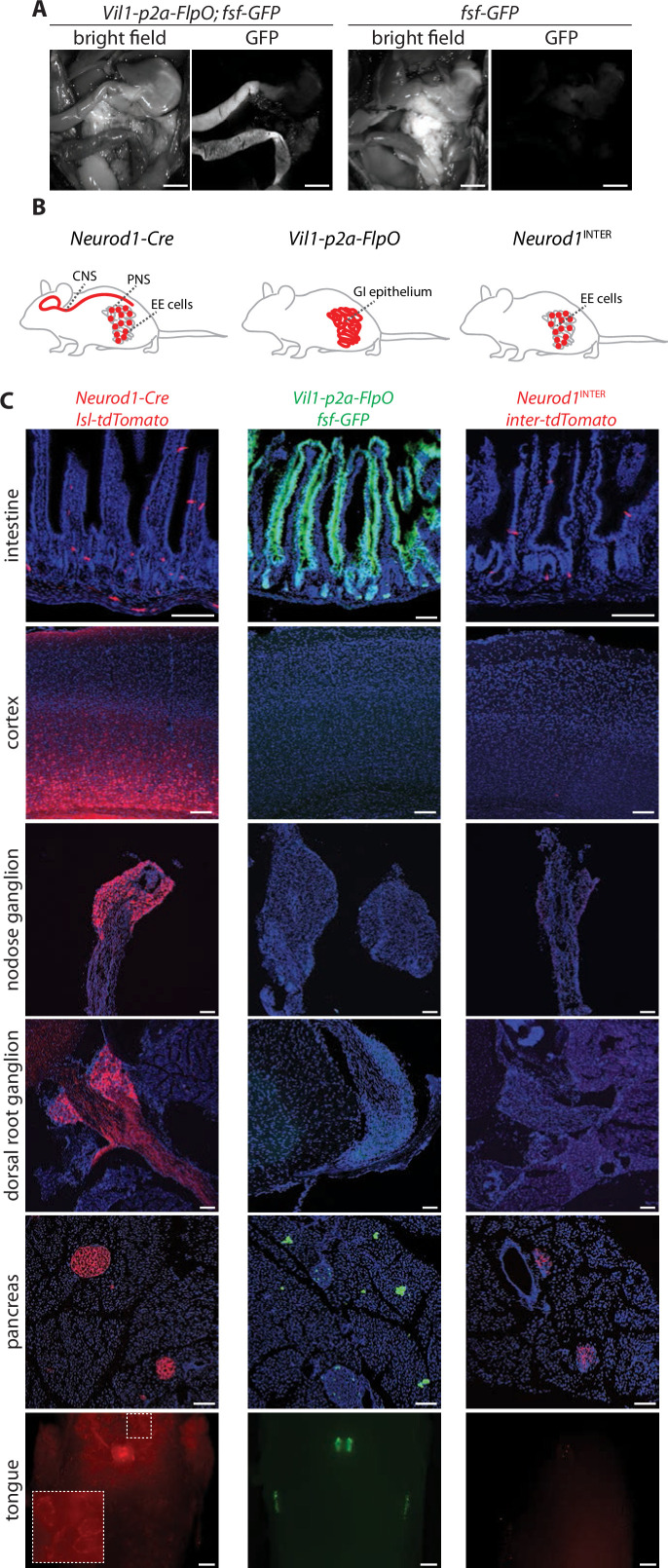
Figure 1. Establishing intersectional tools for genetic access to enteroendocrine cells in vivo.
(A) Bright-field microscopy and native GFP fluorescence microscopy of intestinal tissue from Vil1-p2a-FlpO; fsf-Gfp mice (left) and fsf-Gfp mice (right). Scale bars: 5 mm. (B) Cartoon depicting intersectional genetic strategy to access enteroendocrine cells. (C) Native reporter fluorescence in cryosections (20 μm, except 50 μm for cortex and dorsal root ganglion) or wholemounts (tongue) of fixed tissues indicated from Neurod1-Cre; lsl-tdTomato mice (left), Vil1-p2a-FlpO; fsf-Gfp mice (middle), and Neurod1INTER; inter-tdTomato mice (right). Scale bars: 100 μm for all except 500 μm for tongue. Intestine sections from duodenum (middle) or jejunum (left, right). See Figure 1—figure supplement 1.