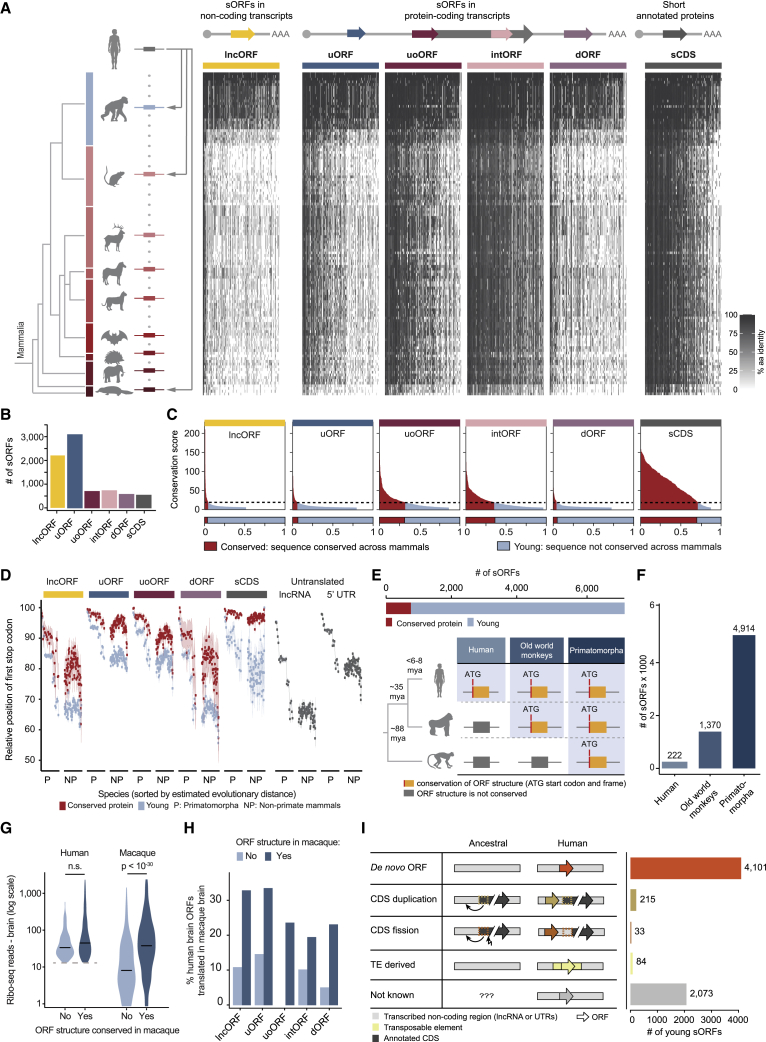
Figure 1.
Most human sORFs are young and have emerged de novo
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the mammalian taxa comprising 120 mammalian species used for sORF genomic alignments (n = 7,264). sORFs were classified into lncRNA-ORFs (lncORFs), upstream ORFs (uORFs), upstream overlapping ORFs (uoORFs), internal ORFs (intORFs), and downstream ORFs (dORFs). For comparison, we included 527 sCDS. The heatmap displays the pairwise aa identity (%) of all sORFs and sCDSs (columns) across the 120 species’ genomes (rows).
(B) Numbers of evaluated sORFs and sCDS separated by ORF biotype.
(C) Conservation scores (CSs) calculated across non-primate mammalian species. Dotted lines represent the CS cutoff of 8 (STAR Methods). sORFs and sCDS with (red) or without (light blue) significant protein sequence conservation are displayed below.
(D) Dot plots displaying the average and 95% confidence interval of sORF, sCDS, and untranslated ORF truncation introduced by the most upstream stop codon in the aligned counterpart regions of the sequences. sORFs are divided by biotype and conservation of aa sequences. Internal sORFs (intORFs) were not considered due to additional constraints acting to preserve the frame of the sequence.
(E) Top: total numbers of conserved (CS ≥ 8) and young sORFs (CS < 8). Bottom: schematic of the classification of young sORFs (n = 6,506) based on conservation of ORF structures. We defined three levels of conservation: humans, old world monkeys, and primatomorpha.
(F) Numbers of evolutionarily young sORFs per level of conservation of ORF structures.
(G) Violin plots with the numbers of human23 (left) and macaque23 (right) brain Ribo-seq reads mapped to human brain translated ORFs (n = 830), by absence (light blue) or presence (dark blue) of conservation in macaque. Statistical differences were assessed by Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Horizontal bars represent the median values. ns, not significant.
(H) Percentages of sORFs translated in the human brain with aligned counterpart regions translated in macaque. sORFs are divided by biotype and by the presence (dark blue) or absence (rlight blue) of conservation in macaques.
(I) Schematic of modes of sORF evolution and numbers of young sORFs per category.