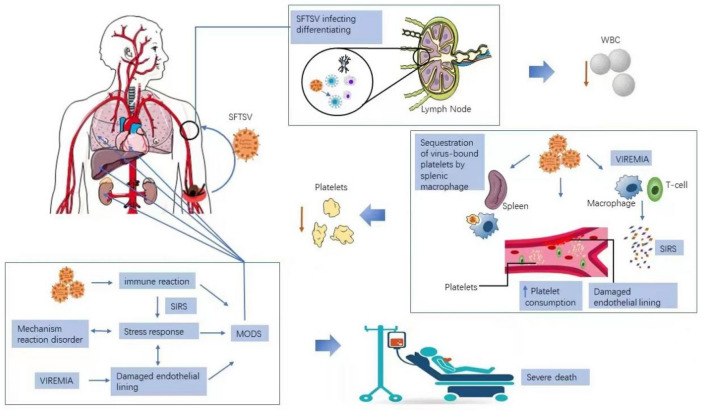
Fig. 2.
The mechanism of SFTSV pathogenesis. SFTSV transmission to humans commonly occurs from virus-carrying-tick-bite. The SFTSV then invades the lymph node nearest to the tick-bite wound, targeting immune cells such as B-cells, impairing host immune response from invading pathogen.It also leads to a decrease in white blood cells.After further replication, the virus goes to the systemic circulation, in response to viremia, other immune cells are over-stimulated causing cytokine storm and severe inflflammatory response syndrome(SIRS). SIRS causes damage to the vascular endothelium, which allows platelets to adhere and aggregate.Thrombocytopenia is a hallmark of SFTSV infection.Body response disorder and stress response caused by cytokine storm lead to multi-organ dysfunction, reflflected by the elevation of liver, kidney, and heart serum markers. Severe cases often die from MODS