Figure 1: Cognitive Benefits of Yoga: Potential Neurocognitive and Stress-Regulating Mechanisms.
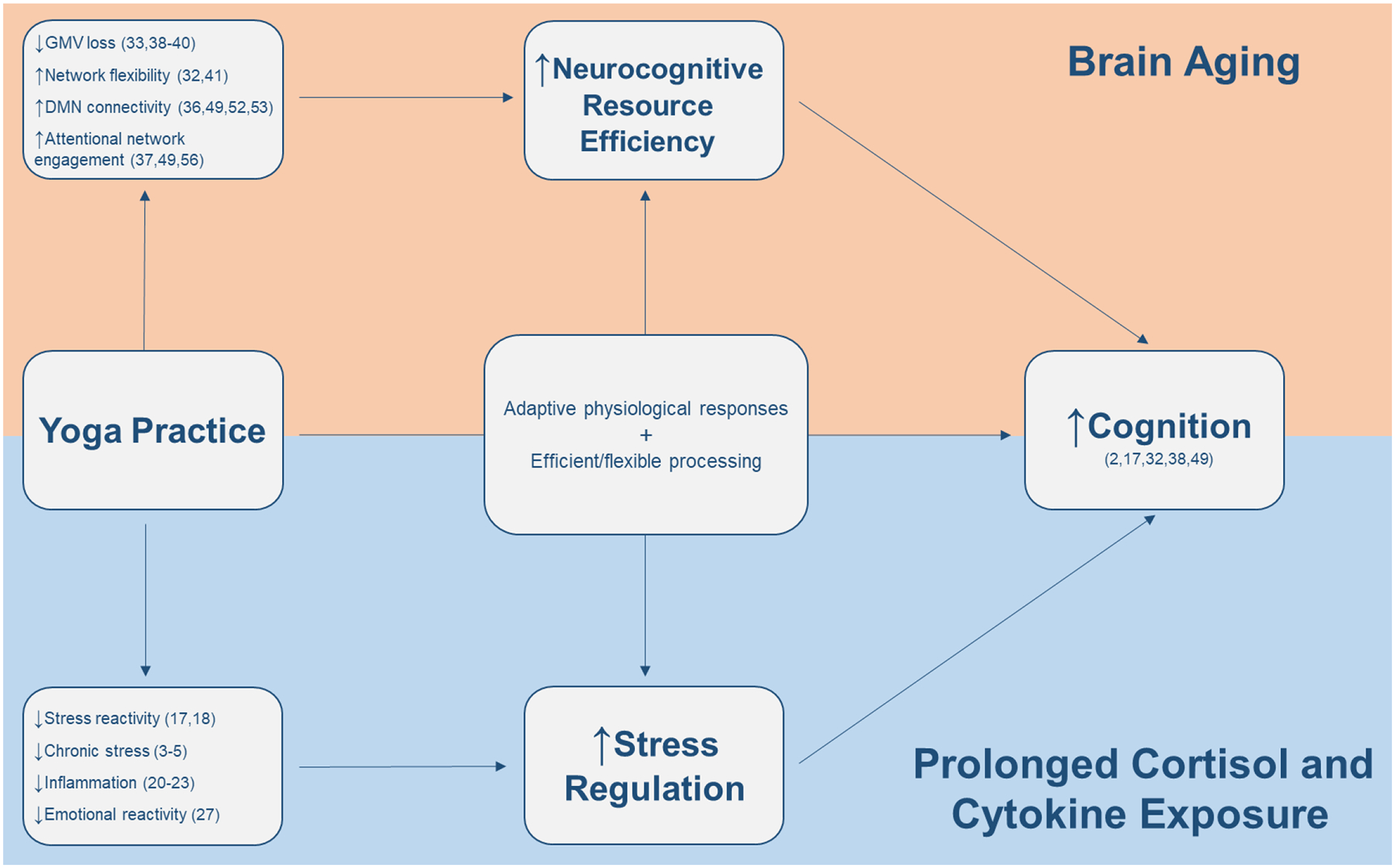
Cognitive deficits occur in the context of age-related cognitive decline (1) and prolonged cortisol and cytokine exposure (8,11). Yoga practice may improve stress regulation and neurocognitive resource efficiency, providing the practitioner with more adaptive physiological responses to stressors along with more efficient and automatic cognitive processing. Improved stress regulation may blunt the deleterious effects of prolonged cortisol exposure associated with chronic stress; and improved neurocognitive resource efficiency may provide neuroprotective benefits to limit age-related cognitive decline. A mindful movement practice, yoga facilitates the integration of top-down neurocognitive and bottom-up physiological processes by combining physical postures with meditation and breathing techniques. GMV; gray matter volume; DMN; Default mode network.
