Figure 6. Mutations near the N- and C-termini alter filament formation which correlates with catalysis.
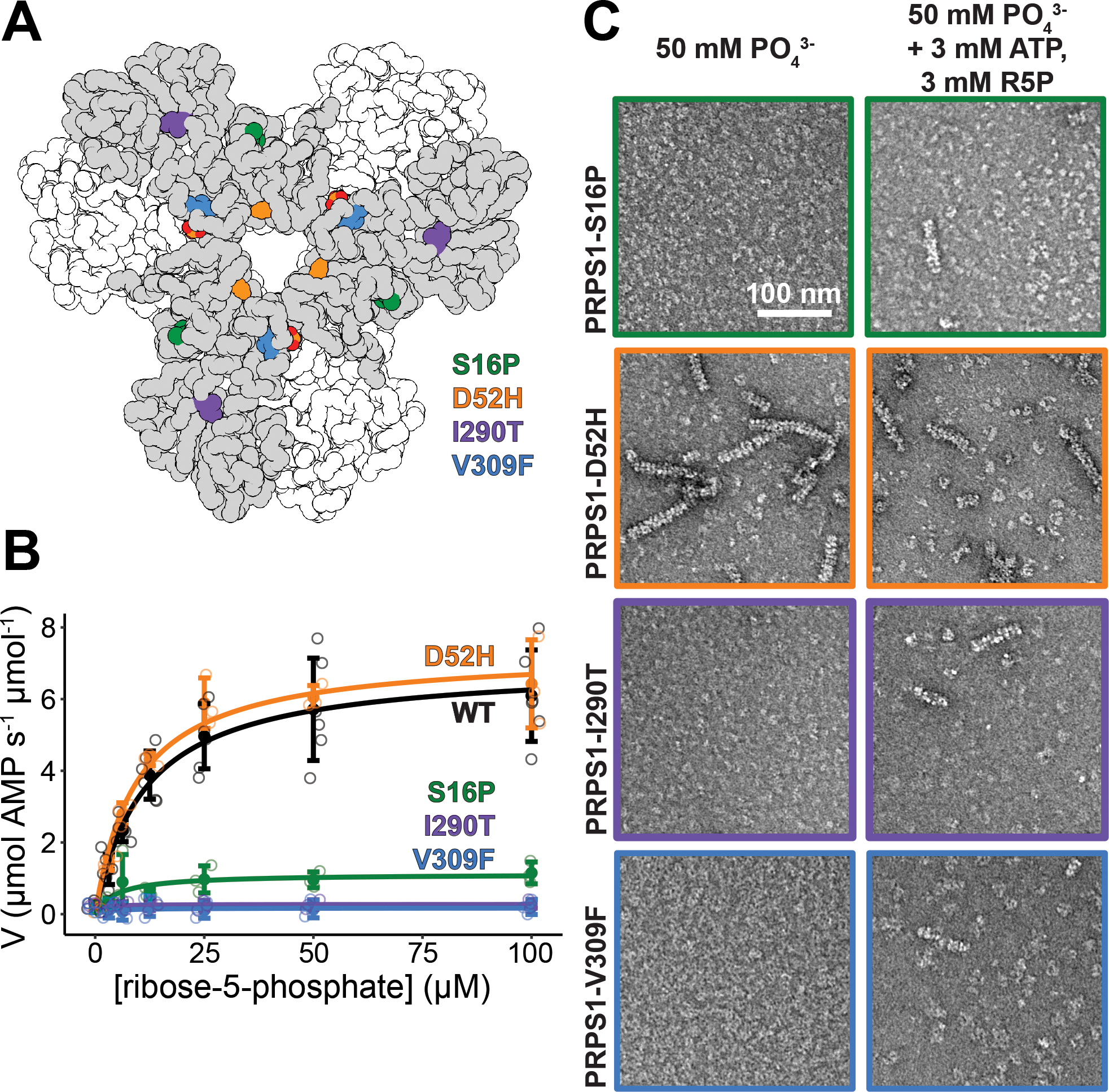
A. Locations of the four mutations that cause disease: S16P, D52H, I290T, and V309F. B. Substrate kinetics of the wild type protein and the four mutations at equimolar protein concentration. Individual data points are shown as open circles. Solid circles and error bars represent mean ± standard deviation (PRPS1: N = 6 technical replicates; Disease Mutants: N = 3 technical replicates). C. Sections of negative stain electron micrograph of the four disease mutations in the presence of phosphate (left) and in the presence of phosphate, ATP, and ribose-5-phosphate (right).
