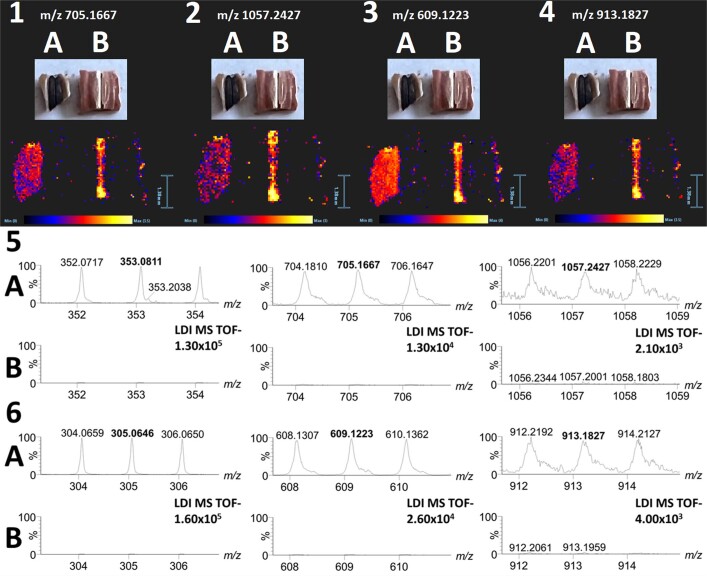
Extended Data Fig. 9. Phenolic compounds in faba bean hila.
Laser desorption-ionisation mass spectrometry imaging (LDI-MSI) showing polymerization of phenolic compounds associated with dark hilum colour in faba bean. Distribution of dimer and trimer of chlorogenic acid (1 and 2) and gallocatechin (3 and 4) on the surface of pigmented (A, Hedin/2) and nonpigmented (B, Tiffany) hila. Zoomed spectra of monomer, dimer and trimer of chlorogenic acid (5; signals at m/z 353.0811; 705.1667 and 1057.2427) and gallocatechin (6; signals at m/z 305.0646, 609.1223, 913.1827) collected from pigmented (A, Hedin/2) and non-pigmented (B, Tiffany) hila (the spectra showing particular signals are zoomed on the same intensity for both genotypes, A and B, e.g. the intensity 1.30x105 is set for spectra 5A and 5B, etc.), spectra were collected from the compact surface without the hilar groove area and edges of the seed coat fragment. The identity of chlorogenic acid and gallocatechin dimers and trimers was further confirmed by characteristic fragments observed during related MS/MS experiment (i.e. anions of caffeic and chlorogenic acids cleaved from chlorogenic acid dimer and trimer at m/z 179.0341 and 353.0811, respectively, and products of retro-Diels Alder cleavage at m/z 179.0375 and 125.0232 from gallocatechin dimers and trimers, respectively).