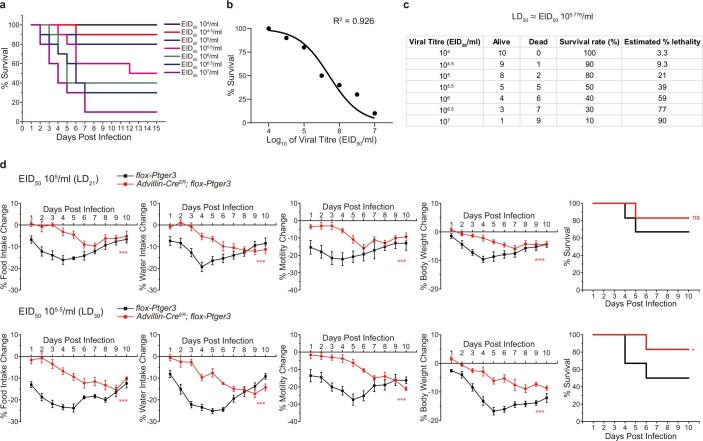
Extended Data Fig. 5. Ptger3 knockout in peripheral sensory neurons attenuates behavioral responses to sublethal influenza A doses.
a, Wild type mice were infected with influenza A virus at titers indicated and subsequent survival monitored daily, n: 10 per group. b, a dose-response curve of viral titer (log10) vs. survival rates with non-linear fit of R2 = 0.926. c, A table indicating survival rates to various influenza A virus inoculation doses, with the estimated % lethality determined by Probit regression analysis (Statistical Product and Service Solutions). d, Advillin-CreER; flox-Ptger3 mice (red, previously injected with tamoxifen) or flox-Ptger3 mice (black) indicated were infected with sublethal doses of influenza A virus (top: 105 EID50 or LD21, bottom: 105.5 EID50 or LD39) and monitored daily as indicated, mean ± sem, n: 6 mice per group, ***p < 0.0005 by two-tailed unpaired t-test as detailed in Fig. 1 for behavior/physiology analysis, *p < 0.05, ns: not significant by a log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test for survival analysis. p values left to right in d, top: <0.0001, <0.0001, 0.0002, <0.0001, 0.4788; bottom: <0.0001, <0.0001, 0.0004, 0.0004, 0.0078.