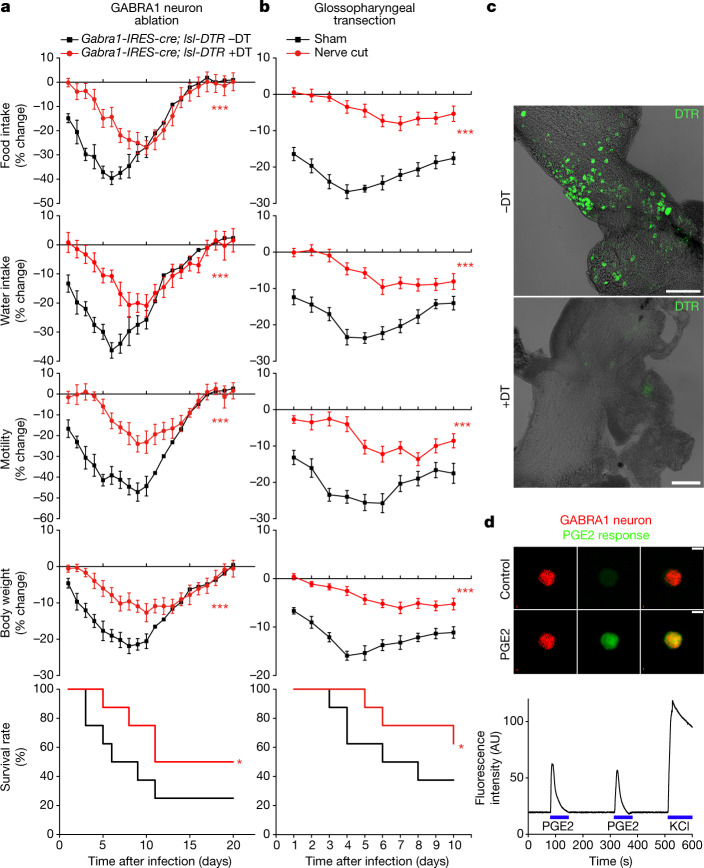
Fig. 4. PGE2 acts via glossopharyngeal sensory neurons.
a, Gabra1-IRES-cre; lsl-DTR mice were injected bilaterally in NJP ganglia with or without diphtheria toxin (DT) and then infected with influenza A virus and monitored as indicated. Data are mean ± s.e.m.; n = 8 mice per group. Food intake: P < 0.0001; water intake: P < 0.0001; motility: P < 0.0001; body weight: P = 0.0004; survival: P = 0.049. b, Wild-type mice with bilateral glossopharyngeal nerve transection surgery or sham surgery were infected with influenza A virus and monitored as indicated. Data are mean ± s.e.m.; n = 8 mice per group. Food intake: P < 0.0001; water intake: P < 0.0001; motility: P < 0.0001; body weight: P < 0.0001; P = 0.036. Two-tailed unpaired t-test as detailed in Fig. 1 for behaviour or physiology analysis; log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test for survival analysis. c, Immunostaining for DTR in whole-mount preparations of NJP ganglia four weeks after injection. Scale bars, 200 μm. d, Calcium transients evoked by PGE2 (1 μM) or KCl (150 mM) were imaged using Calbryte 520 AM in tdTomato-positive neurons acutely collected from NJP ganglia of Gabra1-IRES-cre; lsl-tdTomato mice. Scale bar, 10 μm. Images are representative of three technical replicates. AU, arbitrary units.