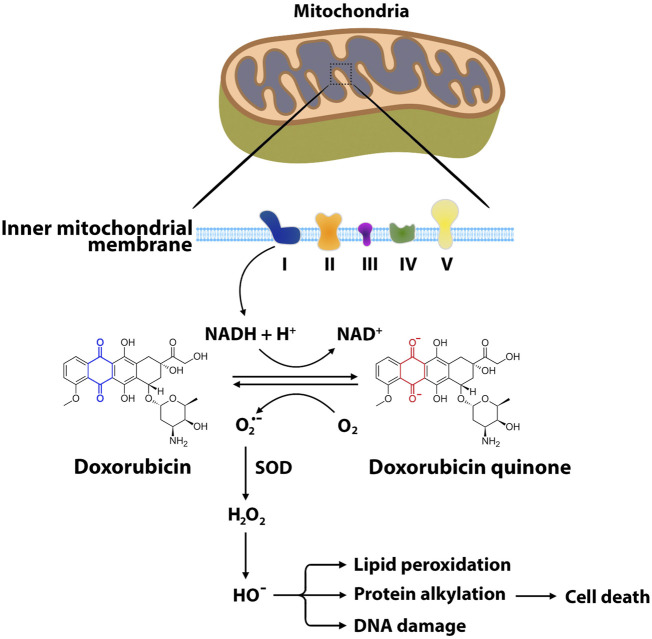
FIGURE 3.
Main pathways of ANT-induced oxidative stress. The formation of reactive oxygen species begins with one-electron reduction of the quinone moiety through NADH reductase at complex I of the electron transport chain. In this reaction, the quinone ring of ANTs such as doxorubicin accepts the electron to form semiquinone, producing superoxide anion. Superoxide dismutase neutralizes the superoxide anion into hydrogen peroxide. Hydroxyl radical is produced from hydrogen peroxide through enzyme-mediated reduction-oxidation cycles. ROS interact with mitochondrial DNA, proteins, lipids, and other biomolecules, leading to cellular oxidative damage and eventually apoptosis. O2 •−, superoxide radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; HO•, hydroxyl radical; SOD, superoxide dismutase; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.