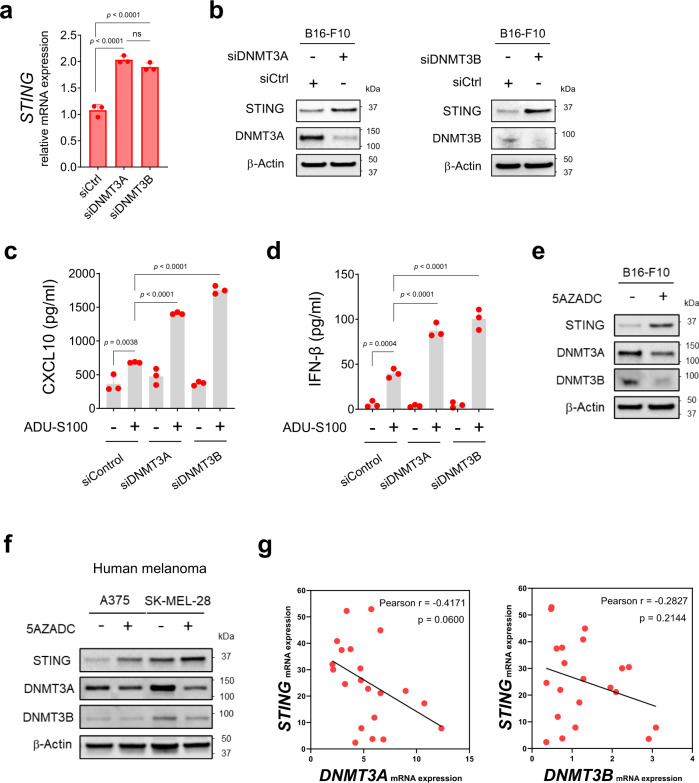
Fig. 3. DNMT3A and DNMT3B are involved in STING silencing in melanoma.
Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of STING mRNA expression in transfected B16-F10 cells with siRNA specific for DNMT3A (siDNMT3A) or DNMT3B (siDNMT3B) or nontarget siRNA (siControl) (n = 3). Data are shown as mean ± SD and are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA (a) (ns, not significant). Immunoblot analysis of STING, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B expression in indicated cells. β-Actin was used as a loading control (b). Levels of CXCL10 (c) and IFN-β (d) in cell culture supernatants measured using ELISA and reported as mean ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Data are representative of two independent experiments (c, d). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. Immunoblot analysis of STING, DNMT3A and DNMT3B expression in B16-F10 (e) and A375 and SK-MEL-28 human melanoma cell lines (f) with or without 5AZADC treatment. Images in (b) and (e–f) are representative of three independent experiments. Correlative analysis of STING mRNA expression with DNMT3A and DNMT3B in metastatic melanoma samples (n = 21) from cBioPortal database using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. P-values shown are two-sided P-values derived from the Pearson correlation test (g).