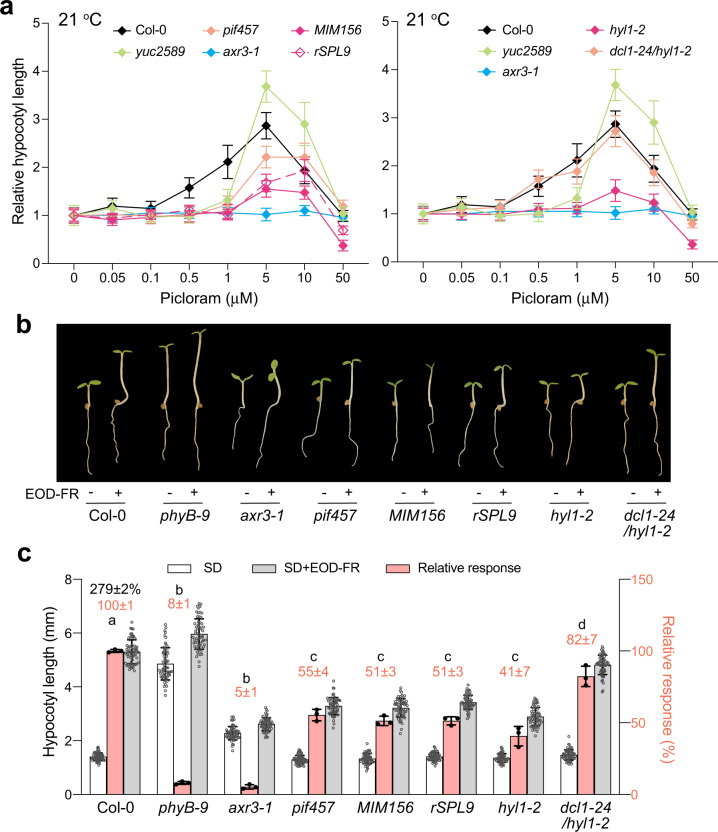
Fig. 6. MiR156-dependent auxin sensitivity is required for the shade avoidance response.
a Auxin dosage response curves showing that miR156 is required for the hypocotyl’s responsiveness to auxin at 21 °C. Hypocotyl length measurements of 4-d-old Col-0, yuc2589, axr3-1, pif457, MIM156, rSPL9, hyl1-2, and dcl1-24/hyl1-2 seedlings grown under 50 μmol m−2 s−1 R light at 21 °C and treated with a concentration series of picloram from 0 to 50 μM. Hypocotyl length was calculated relative to that without picloram treatment for each genotype. Error bars represent the s.d., n = at least 30 seedlings. The centers of the error bars indicate the mean. b Images of 4-d-old Col-0, phyB-9, axr3-1, pif457, MIM156, rSPL9, hyl1-2, and dcl1-24/hyl1-2 seedlings grown at 21 °C under the short-day condition of 8 h of 100 μmol m−2 s−1 white light and 16 h of dark with or without a 15 min end-of-day FR (EOD-FR) light treatment. c Hypocotyl length measurements of seedlings in (a) and their relative response to the EOD-FR treatment. The black number above the Col-0 columns represents the percent increase in hypocotyl length (mean ± s.d., n = 3 biological replicates) by the EOD-FR treatment. The pink bars show the EOD-FR response of a mutant relative to that of Col-0 (set at 100%). Pink numbers show the mean ± s.d. of the relative responses. Different lowercase letters above the bars denote statistically significant differences in the relative responses (ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD, p < 0.01, n = 3 biological replicates). Error bars for the relative responses represent the s.d. of three biological replicates. The centers of all error bars indicate the mean. The source data underlying the hypocotyl measurements in (a) and (c) are provided in the Source Data file.