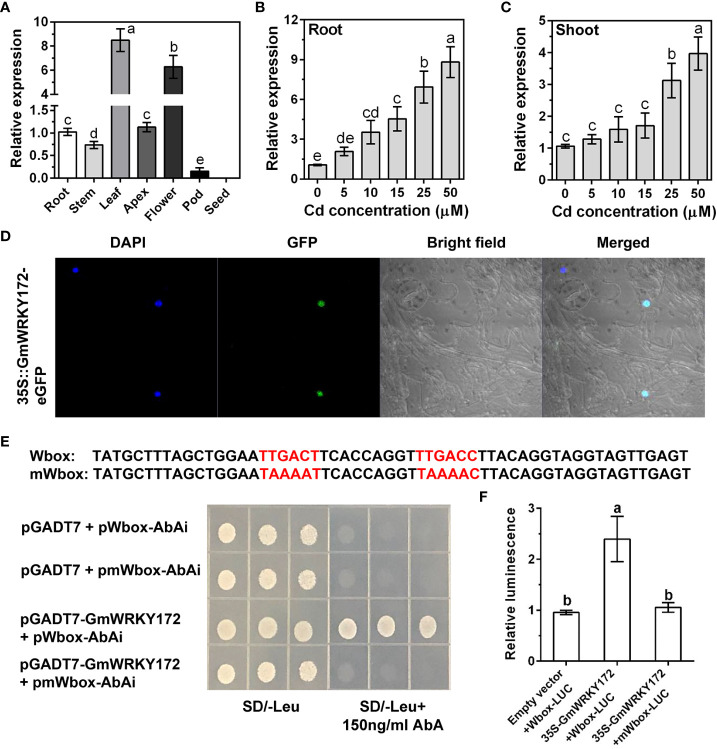
Figure 1.
Expression patterns, subcellular localization, and transcriptional activity assays of GmWRKY172. (A) Expression analysis of GmWRKY172 in different tissues of soybean by quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR). Dose-dependent expression of GmWRKY172 in roots (B) and leaves (C). Samples were exposed to different Cd concentrations (0, 5, 10, 15, 25 and 50 µM) for 4 hours. (D) Subcellular localization of GmWRKY172 in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells. (E) Yeast one-hybrid analysis for interaction between GmWRKY172 and W-box motifs. The Y1HGold yeast strain was co-transformed with the prey (pGADT7 or pGADT7-GmWRKY172) and the bait (pAbAi-Wbox or pAbAi-mWbox). SD medium lacking leucine with 150 ng/mL AbA was used to determine the interaction between the bait and prey proteins. (F) Transcription activity assay in Nicotiana benthamiana to examine the interaction between GmWRKY172 and W-box motifs. The relative luminescence was determined by normalizing firefly luciferase activity with Renilla luciferase activity. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate statistical significance determined by one-way analysis of variance and Duncan’s test (P ≤ 0.05).