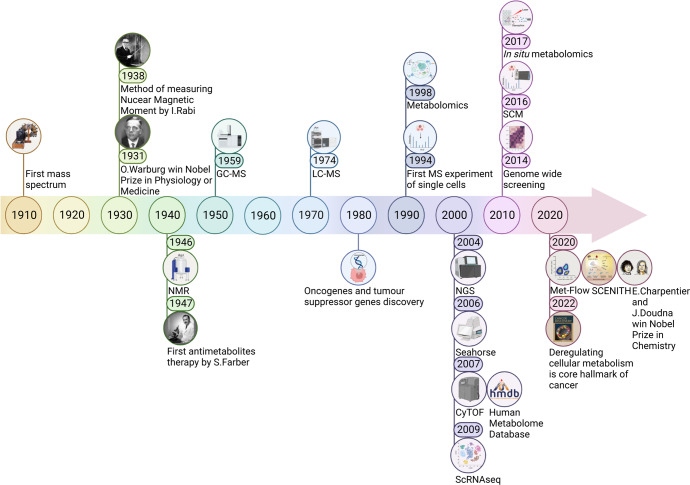
Fig. 1.
Timeline of the milestone events for cancer metabolism. The first mass spectrum of a molecule was measured by Joseph J. Thomson in 1910. In 1931 Otto H. Warburg won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for characterizing the respiratory enzyme. In 1938 Isidor I. Rabi detected the Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) for the first time in a beam of lithium chloride thus developing the methodology and further expanded in 1946 by Felix Bloch and Edward M. Purcell for use on liquids and solids. Gas chromatography (GC)-MS was described in 1959 and Liquid chromatography (LC)-MS was introduced in 1974. The discovery of oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes dates back to the 1980s. In 1994 Tsutomu Nomizu and colleagues realized the first single cells MS experiment, while in 1998 Steven Oliver firstly introduced the concept of metabolomics. 2004 is the year of Next-generation sequencing (NGS), 2006 of the Seahorse real-time cell metabolic analyser, 2007 of the first prototype of Cytometry by Time-of-flight (CyTOF) and of the first version of The Human metabolome database (HMDB). In 2009 there was the development of Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq), in 2016 of Single-cell metabolomics (SCM) and in 2017 of the In situ metabolomics. The first genome-wide functional screening was performed in 2014 and in 2020 Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for discovering the CRISPR/Cas9 system. In 2020 the flow-cytometry-based technologies Met-flow and SCENITH have been proposed. In 2022 the deregulation of cellular metabolism was eventually recognized core hallmark of cancer by Douglas Hanahan. This figure was created with Biorender.com