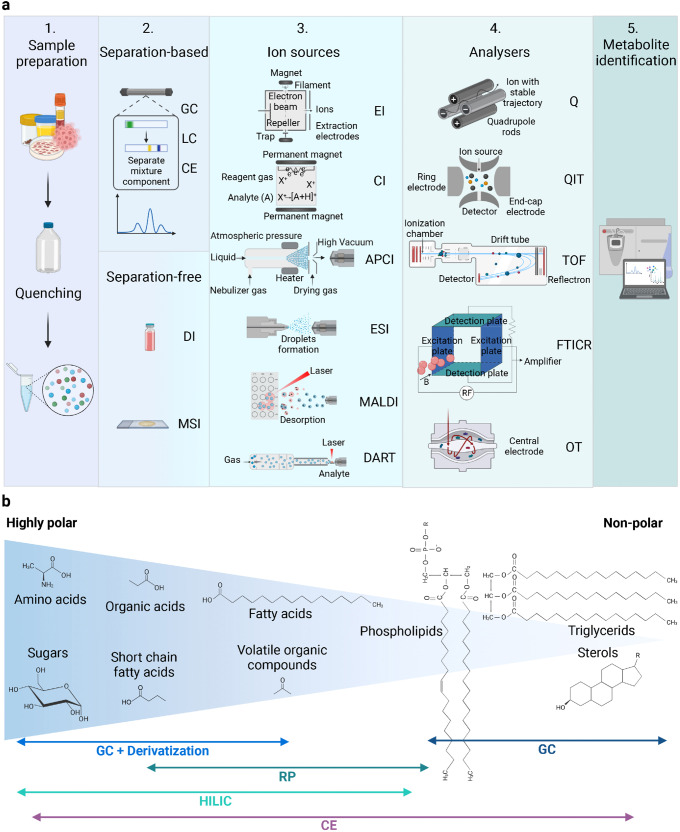
Fig. 2.
a Mass spectrometry (MS)-metabolomic workflow. 1. Samples preparation consists of metabolism quenching and metabolites extraction. 2. Metabolites may need a separation step with Gas chromatography (GC), Liquid chromatography (LC), Capillary electrophoresis (CE) or can be directly ionized in the Direct infusion (DI) and in the Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI). 3. Different ionization techniques can be employed: Electron impact ionization (EI), Chemical ionization (CI), Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI), Electrospray ionization (ESI), Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) and Direct real-time analysis (DART). 4. Single (MS) or tandem (MS/MS) mass analysers can be alternatively employed to separate ions according to their m/z: Quadrupole (Q), Quadrupole ion trap (QIT), Time-of-flight analyser (TOF), Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR), Orbitrap (OT). 5. Data processing includes conversion of m/z values, detection, filtering, normalization and identification. b Schematic depicting the most suitable techniques to separate metabolites with distinct polarity. This figure was created with Biorender.com