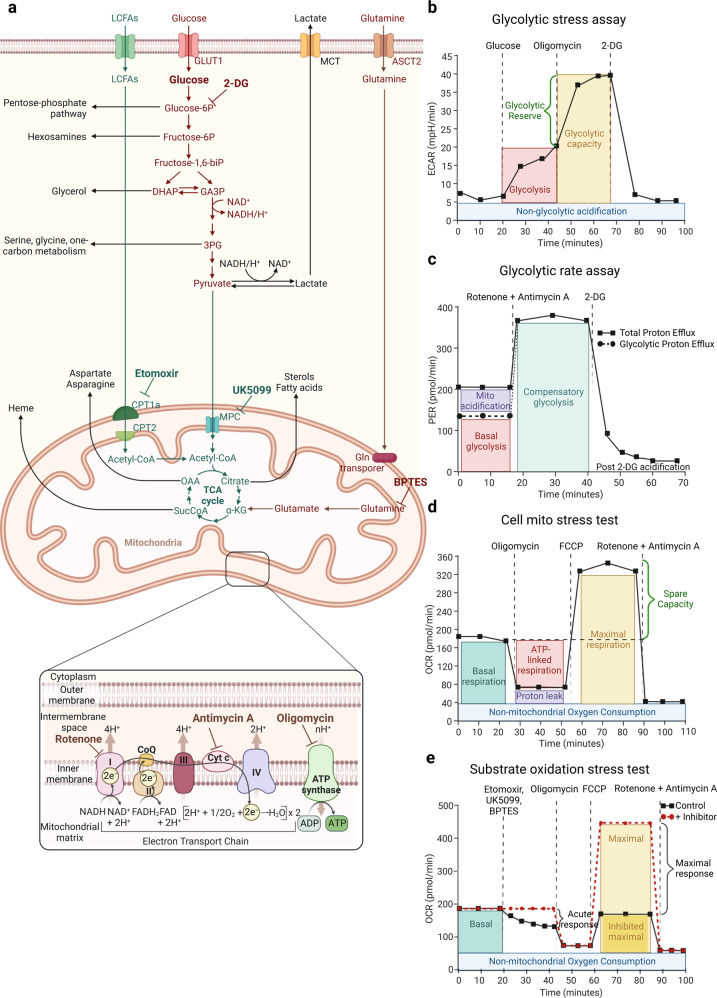
Fig. 4.
a Key metabolic pathways governing cancer cell growth that can be measured by Extracellular flux analysis (EFA). b Glycolysis stress assay is performed by serial injections of Glucose, Oligomycin and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) to get as a read out glycolysis, glycolytic capacity, the glycolytic reserve and non-glycolytic acidification measurements. ECAR stands for extracellular acidification rate. c The Glycolytic rate assay reports multiple key parameters, such as basal glycolysis, compensatory glycolysis achieved by shutting down mitochondrial respiration with rotenone and antimycin A. Proton efflux rate (PER) is a quantitative measure of protons extruded into the extracellular medium during glycolysis. d In the Cell mito stress test, mitochondrial respiration is measured by quantifying the Oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Cells are sequentially exposed to oligomycin, Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP) and rotenone and antimycin A thus allowing the measurement of the basal and maximal respiration and spare respiratory capacity. e The Substrate oxidation stress test measures the contribution of Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), glucose/pyruvate and glutamine as primary substrates that fuel mitochondrial metabolism by using specific inhibitors in combination with a standard Cell mito stress assay. Etomoxir inhibits the Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1a (CPT1a), UK5099 blocks glucose and/or pyruvate through inhibition of the Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) and BPTES inhibits glutamine through Glutaminase-1 (GLS-1). This figure was created with Biorender.com