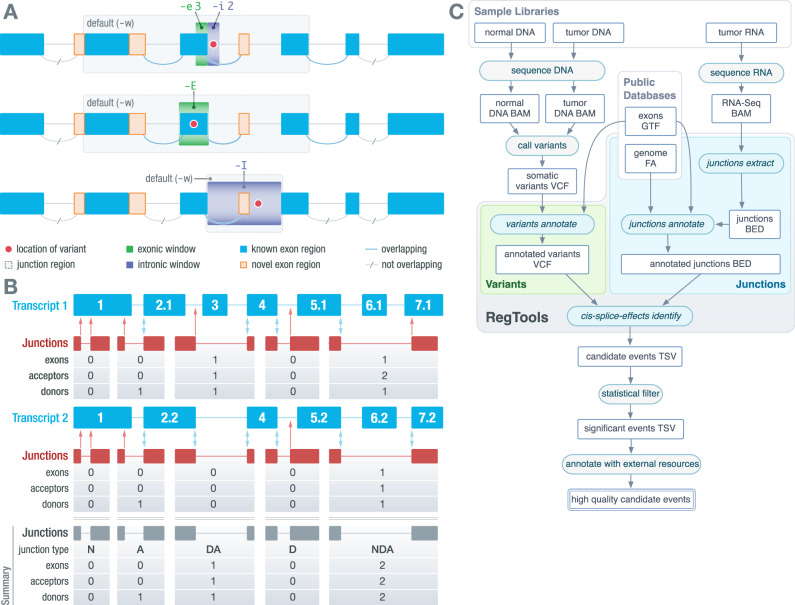
Fig. 1. RegTools features individual modules and an integrated pipeline for flexible, streamlined discovery of cis-acting splice-associated variants.
A A schematic depicting how variants (red dots) are associated to exon-exon junctions (curves). By default, variants annotate marks variants within 3 bp on the exonic side (green box) and 2 bp on the intronic side (purple box) of an exon edge as potentially splice-associated. Within cis-splice-effects identify, a “splice junction region” is determined by finding the largest span of sequence space between exons that flank the exon associated with the splicing-relevant variant. Junctions overlapping the splice junction region are associated with the variant. Using the “-E” or “-I” option considers either all exonic variants or all intronic variants, respectively, as potentially splice-associated. B A schematic depicting how RegTools annotates exon-exon junctions with respect to known transcripts. Cis-splice-effects identify and the underlying junctions annotate command annotate junctions based on whether the donor and acceptor site combination is found in the reference transcriptome GTF. In this example, there are two known transcripts (shown in blue) that overlap a set of junctions observed in RNAseq data (depicted as junction supporting reads in red). RegTools checks to see if the observed donor and acceptor splice sites are found in any of the reference exons and counts the number of exons, acceptors, and donors skipped by a particular junction. Double blue arrows represent matches between observed and reference donor/acceptor sites, while single red arrows show non-reference splice sites. Junctions with a known donor but unknown acceptor or vice-versa are annotated as “D” or “A”, respectively. If both sites are known but do not appear in combination in any transcripts, the junction is annotated as “NDA”, whereas if both sites are unknown, the junction is annotated as “N”. If the junction is known to the reference GTF, it is marked as “DA”. C A schematic depicting the overall RegTools analysis workflow. The cis-splice-effects identify command relies on the variants annotate, junctions extract, and junctions annotate submodules. This pipeline takes variant calls and RNA-seq alignments along with genome and transcriptome references and outputs information about events (pairs of variants and associated junctions). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. ‘BAM’ refers to a binary alignment map file. ‘GTF’ refers to the gene transfer format. ‘VCF’ refers to the variant call format. ‘FA’ refers to fasta format. ‘BED’ refers to browser extensible data. ‘TSV’ refers to tab separated value format.