Figure 3.
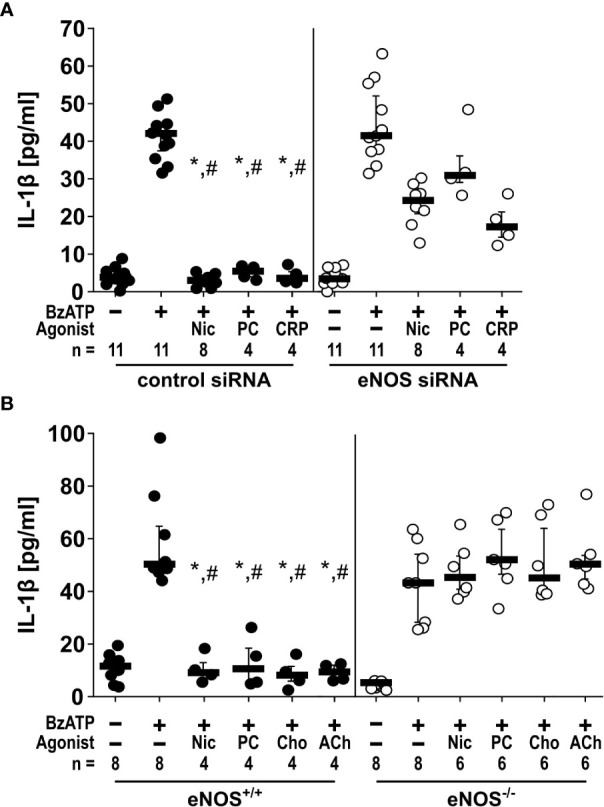
The inhibitory potential of cholinergic agonists on BzATP-induced IL-1β release by monocytic cells depends on endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS, NOS3) activity. (A) U937 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting eNOS or with control siRNA. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 µg/ml) for 5 h and BzATP ((2’/3’-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine-5’-triphosphate, tri(triethylammonium) salt; 100 µM) was given for additional 30 min in the presence or absence of nicotinic agonists nicotine (Nic; 100 µM), phosphocholine (PC; 100 µM) or C-reactive protein (CRP; 5 µg/ml). While in cells transfected with control siRNA, the BzATP-induced release of IL-1 β was inhibited by nicotinic agonists, the inhibitory activity of all agonists was blunted in eNOS siRNA-transfected cells. Data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Mann-Whitney rank sum test. (B) Freshly isolated mouse peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from wild-type (eNOS+/+) mice and mice deficient in eNOS (eNOS-/-) were left untreated or stimulated with BzATP for 30 min, in the presence or absence of nicotinic agonists Nic, PC, choline (Cho; 100 µM) or acetylcholine (ACh; 10 µM). BzATP induced the release of IL-1β in PBMCs obtained from all mouse strains. Nicotinic agonists significantly inhibited the IL-1β release by PBMCs from eNOS+/+ mice. In contrast, the IL-1β release by PBMCs from eNOS-/- mice was not affected by nicotinic agonists. Friedman test followed by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Data are presented as individual data points, bars represent median, whiskers percentiles 25 and 75. ∗p ≤ 0.05 significantly different from samples, in which BzATP was given alone #p ≤ 0.05 significantly different from corresponding samples control siRNA vs. eNOS siRNA and eNOS+/+ vs. eNOS-/-.
