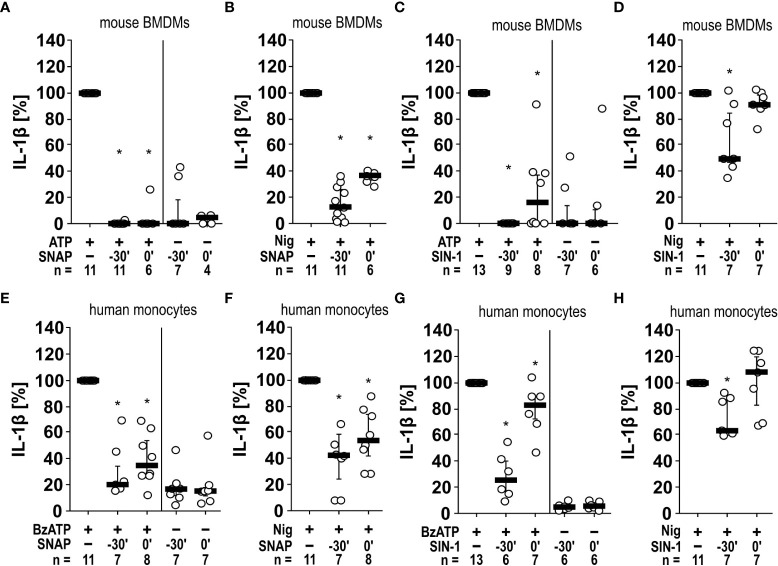
Figure 5.
Inhibition of IL-1β release by the NO donors SNAP and SIN-1 in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and primary human monocytes. (A–D) Mouse BMDMs were primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 µg/ml, 5 h). (A, C) Thereafter, ATP (1 mM) was added for another 40 min to trigger IL-1β release, which was measured by ELISA. Application of the NO donor SNAP (S-nitroso-N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine; 1 mM) 30 min prior to ATP (t = -30´) or shortly before ATP (t = 0´) reversed the ATP-induced release of IL-1β. Similar results were found by using SIN-1 (1 mM). (B, D) To test for P2X7 receptor-independent IL-1β release, nigericin (Nig; 50 µM) was added together with apyrase (0.5 U/ml) for 40 min to LPS-primed mouse BMDMs. The Nig-induced IL-1β release was unimpaired by SIN-1 at t = 0´ and slightly reversed in presence of SNAP and SIN-1 at t = -30´. The amount of IL-1β released in response to ATP/Nig was calculated by subtracting the IL-1β concentrations measured in supernatants of cells treated with LPS alone. ∗ p ≤ 0.05 significantly different from samples, in which ATP or Nig was given alone. (E–H) Similar experiments were performed on primary human monocytes enriched from freshly collected human whole blood. Cells were primed with LPS (5 ng/ml, 20 min pulse) during the enrichment process. After 3 h, BzATP ((2’/3’-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine-5’-triphosphate, tri(triethylammonium) salt; 100 µM); (E, G) or Nig (F, H) was added for another 30 min to trigger IL-1β release. The IL-1β concentration in experiments, in which primed cells were stimulated with BzATP or Nig alone, was set to 100% and all other values were calculated accordingly. ∗ p ≤ 0.05 significantly different from samples, in which BzATP was given alone. (A–H) Data are presented as individual data points, bars represent median, whiskers percentiles 25 and 75. Friedman test followed by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.