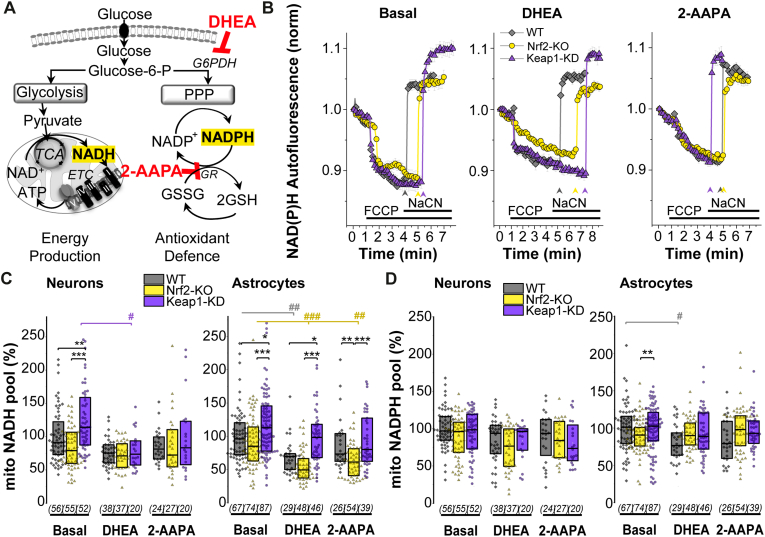
Fig. 6.
Mitochondrial NADH and NADPH levels after inhibition of PPP(A) Scheme showing main pathways of cellular glucose metabolism and the role of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) as an inhibitor of pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) (100 μM, 24 h); and 2-AAPA (50 μM, 24 h) as an inhibitor of glutathione reductase (GR) (B) Representative traces of mitochondrial NADH homeostasis in astrocytes, in the absence/presence of the inhibitors, with arrows indicating the moment NaCN was added. (C) Quantification of the total mitochondrial NADH pool and (D) NADPH pool as measured by the remaining NAD(P)H autofluorescence after consumption of all mitochondrial NADH. Number of cells analysed is shown in brackets. Both are expressed as the % of WT basal. Non parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with post-hoc Dunn's test for each group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001.