Abstract
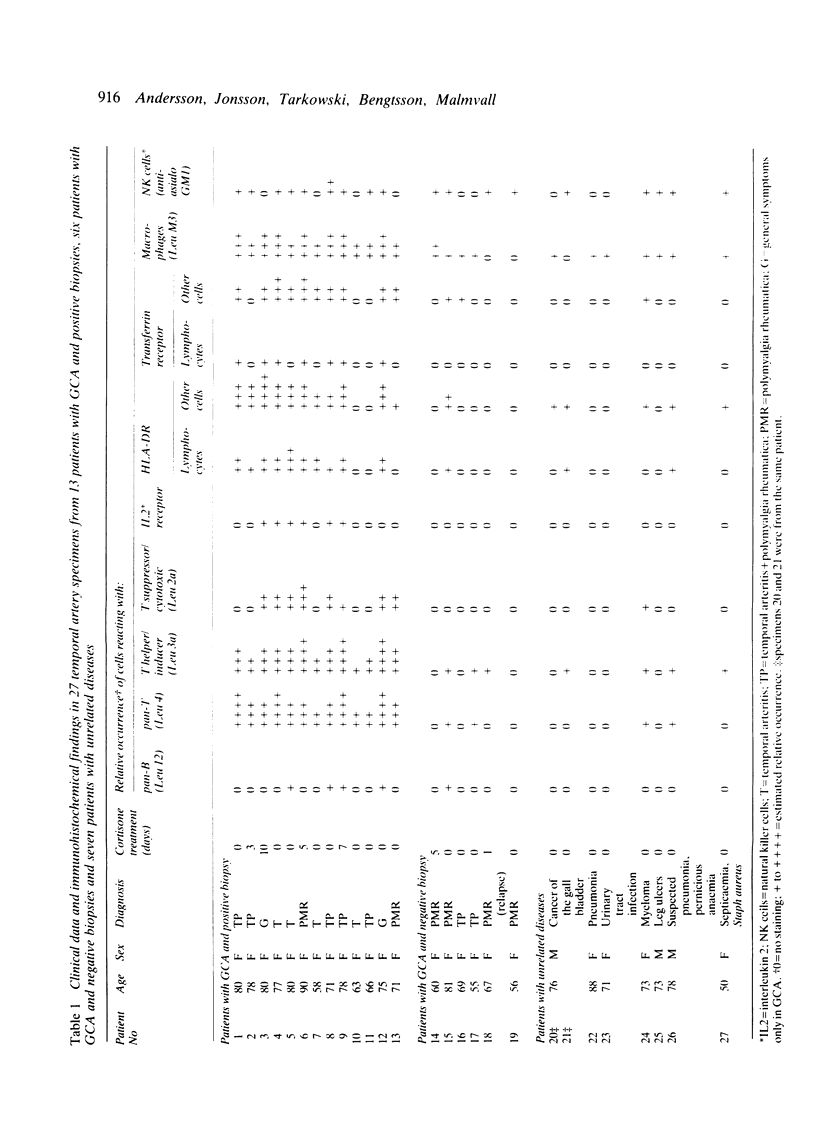
Immunohistochemical features of infiltrating mononuclear cells (MNC) and resident cells were studied in the temporal artery biopsy specimens of 13 patients with histological verified giant cell arteritis (GCA) and in six biopsy specimens from patients with GCA with negative histological findings. Eight temporal artery biopsy specimens from seven patients with unrelated diseases served as controls. In all patients with GCA proved by biopsy an infiltration of T lymphocytes in the arterial wall was observed, most being of the helper/inducer subset. No B lymphocytes, or very few, were seen. Lymphocytes in 10 out of the 13 positive biopsy specimens displayed staining for the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen HLA-DR, whereas this was found in only two of eight controls. A minor number of the infiltrating T lymphocytes from seven out of 13 patients with GCA proved by biopsy stained for transferrin receptors, and in six out of the 13 cases they reacted with anti-interleukin 2 receptor antibody. In the arterial wall from all patients with histologically verified GCA we also found an increased number of macrophages, many of them expressing HLA-DR antigens and transferrin receptors. The immunohistochemical pattern of cell phenotypes found in the arterial wall of patients with GCA suggests that the infiltrating T cells are immunologically activated. This finding supports the hypothesis of a predominantly cellular immunological pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis.
Full text
PDF

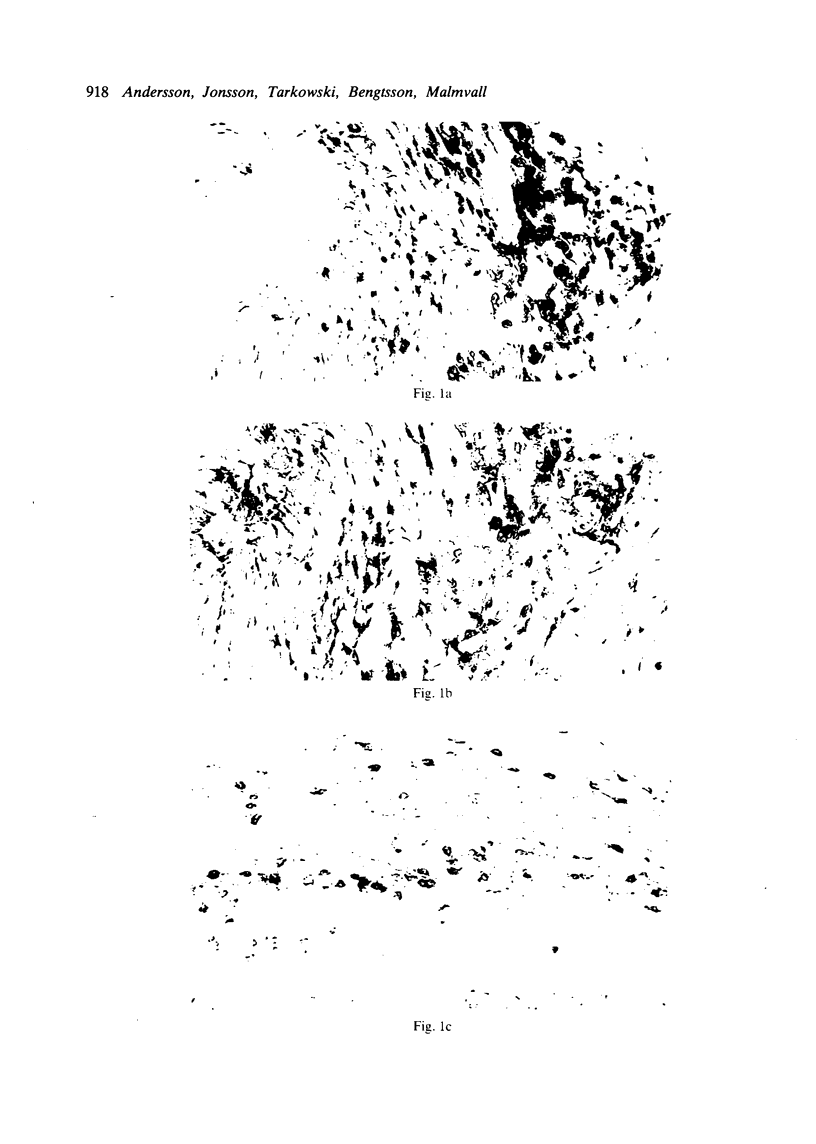
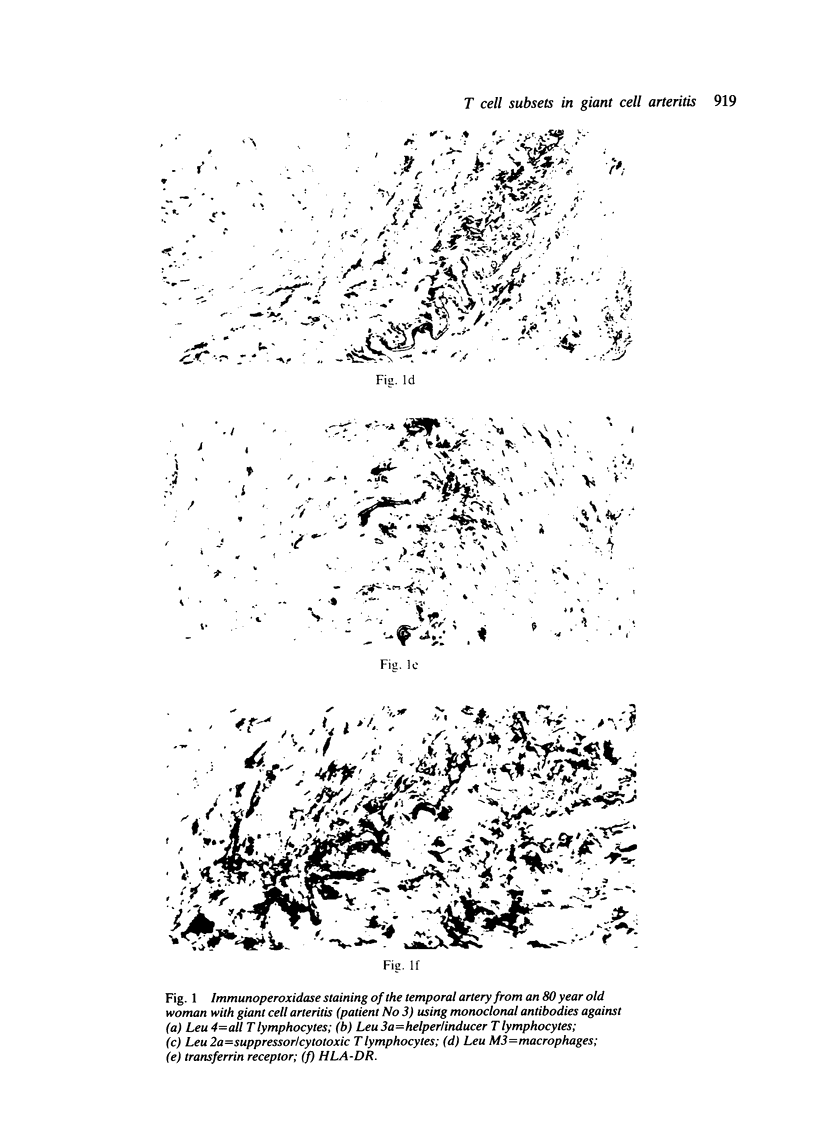
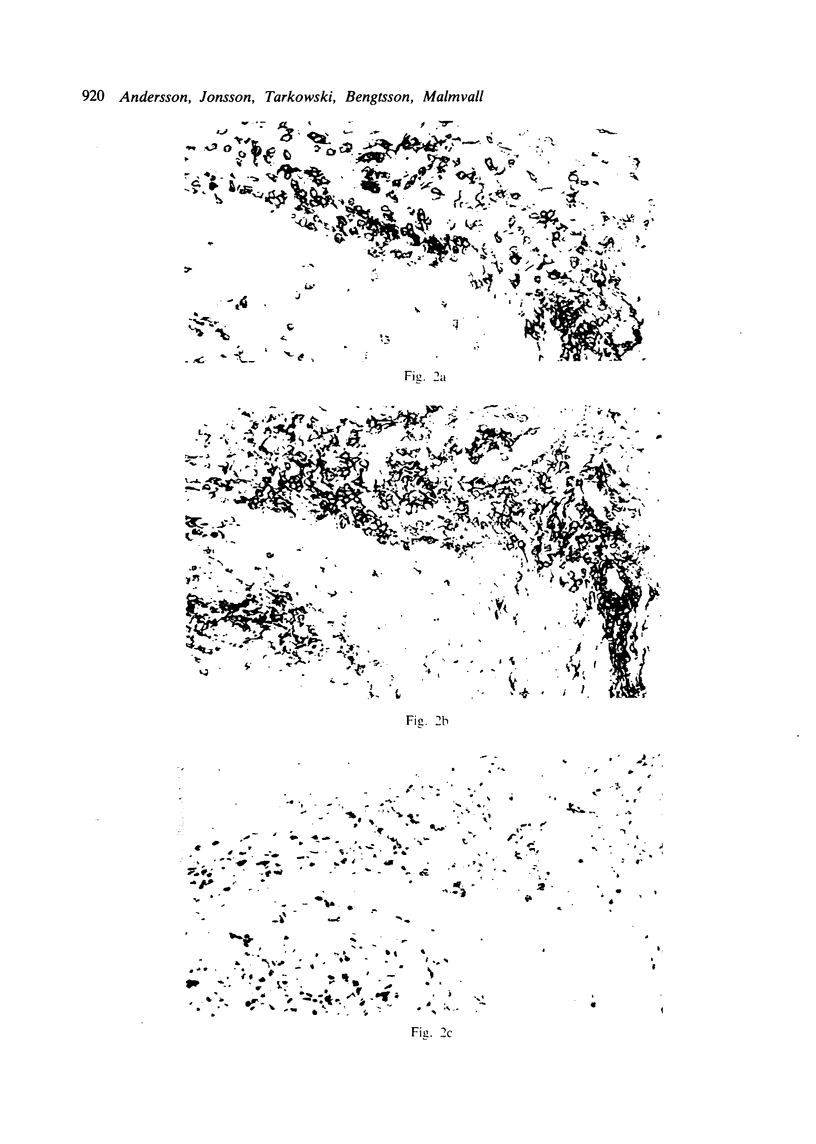
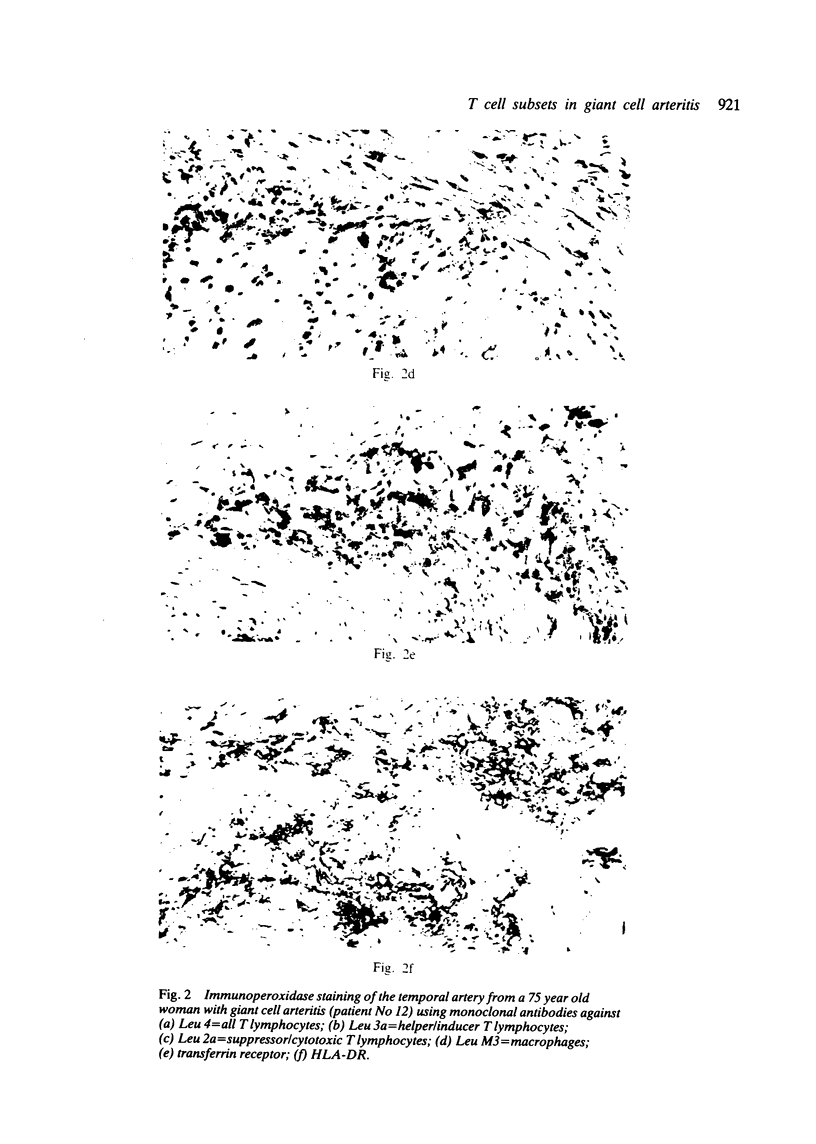


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks P. M., Cohen M. D., Ginsburg W. W., Hunder G. G. Immunohistologic and cytochemical studies of temporal arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1201–1207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. A., Malmvall B. E. The epidemiology of giant cell arteritis including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Incidences of different clinical presentations and eye complications. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jul;24(7):899–904. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benlahrache C., Segond P., Auquier L., Bouvet J. P. Decrease of the OKT8 positive T cell subset in polymyalgia rheumatica. Lack of correlation with disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1472–1480. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelazzi G., Broggini M. Abnormalities of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets in polymyalgia rheumatica. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1984 Oct-Dec;2(4):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess J., Albert D. M., Bhan A. K., Paluck E. I., Robinson N., Collins B., Kaynor B. Serologic and immunopathologic findings in temporal arteritis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Sep;96(3):283–289. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elling H., Elling P. Decreased level of suppressor/cytotoxic T cells (OKT8+) in polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritis: relation to disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):306–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher P., Jones K. Immunohistochemical findings in cranial arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jan;25(1):75–79. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Jonasson L., Holm J., Claesson-Welsh L. Class II MHC antigen expression in the atherosclerotic plaque: smooth muscle cells express HLA-DR, HLA-DQ and the invariant gamma chain. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 May;64(2):261–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson R., Karlsson A., Forsum U. Intrathyroidal HLA-DR expression and T lymphocyte phenotypes in Graves' thyrotoxicosis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis and nodular colloid goitre. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):264–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Skalli O., Bondjers G., Hansson G. K. Regional accumulations of T cells, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells in the human atherosclerotic plaque. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):131–138. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson L., Holm J., Skalli O., Gabbiani G., Hansson G. K. Expression of class II transplantation antigen on vascular smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):125–131. doi: 10.1172/JCI111934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Scheynius A., Kabelitz D., Wigzell H. Evidence in support of a self-perpetuating HLA-DR-dependent delayed-type cell reaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3632–3636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Wigren A., Wigzell H. Relationship between HLA-DR-expressing cells and T lymphocytes of different subsets in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1981 May;15(5):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang G. C., Simkin P. A., Mannik M. Immunoglobulins in temporal arteries. An immunofluorescent study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jul;81(1):19–24. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Hedfors E., Klareskog L., Forsum U. Epithelial HLA-DR expression and T lymphocyte subsets in salivary glands in Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):475–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad S., Klareskog L., Hedfors E., Forsum U., Sundström C. Phenotypic characterization of synovial tissue cells in situ in different types of synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Nov;26(11):1321–1332. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmvall B. E., Bengtsson B. A., Kaijser B., Nilsson L. A., Alestig K. Serum levels of immunoglobulin and complement in giant-cell arteritis. JAMA. 1976 Oct 18;236(16):1876–1878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmvall B. E., Bengtsson B. A., Nilsson L. A., Bjursten L. M. Immune complexes, rheumatoid factors, and cellular immunological parameters in patients with giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):276–280. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Sharrow S. O. HLA-DRw alloantigens can be detected on peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):1889–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Henriksson K. G., Klareskog L., Forsum U. HLA-DR expression, T lymphocyte phenotypes, OKM1 and OKT9 reactive cells in inflammatory myopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Jun;8(5):419–425. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaioannou C. C., Gupta R. C., Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C. Circulating immune complexes in giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Sep;23(9):1021–1025. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papaioannou C. C., Hunder G. G., McDuffie F. C. Cellular immunity in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: lack of response to muscle or artery homogenates. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):740–745. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. R., Hazleman B. L. Immunological and histological study of temporal arteries. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978 Jun;37(3):238–243. doi: 10.1136/ard.37.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. R., Jones J. G., Harkiss G. D., Hazleman B. L. Circulating immune complexes in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Aug;40(4):360–365. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Levey R. H., Schlossman S. F. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1588–1592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Delia D., Schneider C., Newman R., Kemshead J., Greaves M. Ubiquitous cell-surface glycoprotein on tumor cells is proliferation-associated receptor for transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4515–4519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velvart M., Felder M., Fehr K., Sommermeyer G., Cancer M., Wagenhäuser F. J., Böni A. Temporal arteritis in polymyalgia rheumatica: immune complex deposits and the role of the leukocyte elastase in the pathogenesis. Z Rheumatol. 1983 Nov-Dec;42(6):320–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waaler E., Tönder O., Milde E. J. Immunological and histological studies of temporal arteries from patients with temporal arteritis and/or polymyalgia rheumatica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1976 Jan;84(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youinou P. Y., Pennec Y., Tande D., Le Menn G. Immune complexes and autoantibodies in patients with giant cell arteritis and their relationship with autologous rosette-forming cells. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1985 Jan-Mar;3(1):17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]