Fig. 1.
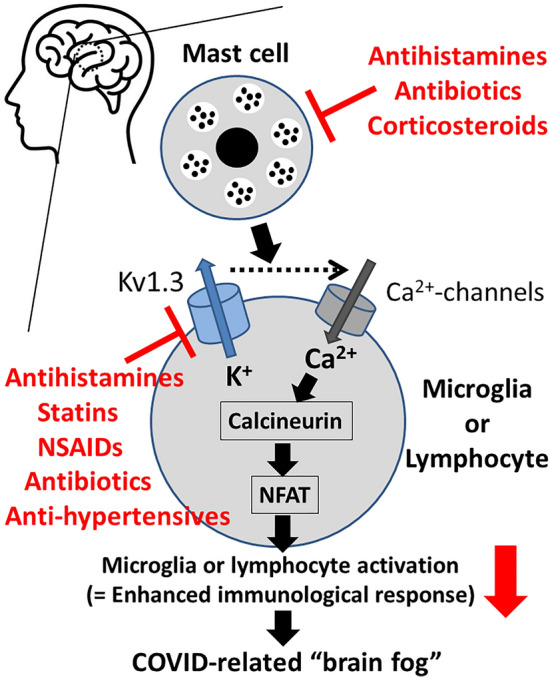
Roles of mast cells and Kv1.3-channels in the activation pathway of brain leukocytes (microglia or lymphocytes) and as the targets of commonly used drugs for COVID-related brain fog. Kv1.3-channels promote calcium influx and trigger the proliferation and activation of brain macrophages (microglia) or lymphocytes. The increased cytosolic calcium concentration stimulates the phosphatase calcineurin, which de-phosphorylates the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), causing its accumulation in the nucleus and binding to the promoter region of cytokine-encoding genes. Antihistamines, statins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics and anti-hypertensives, which inhibit Kv1.3-channels, or antihistamines, antibiotics and corticosteroids, which stabilize mast cells, directly or indirectly suppress the activity of brain leukocytes and the subsequent immunological response
