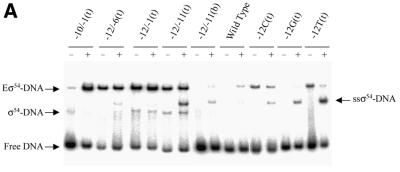
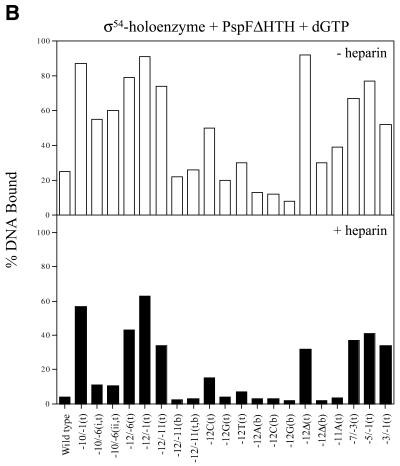
Figure 3.
Activator-dependent formation of σ54 holoenzyme–heteroduplex DNA complexes. Gel shift mobility assays were carried out as described in Figure 2 except that after σ54 holoenzyme DNA binding, activator (PspFΔHTH, 4 µM) and dGTP (1 mM) were added for a further 10 min. (A) Sample gel showing the number of heparin stable σ54 holoenzyme–heteroduplex complexes formed in the absence (–) and presence (+) of PspFΔHTH and dGTP. The sample heteroduplexes are indicated above the lanes. With certain early melted heteroduplexes an additional activator- and nucleotide-dependent supershifted complex (ssσ54–DNA) is seen that has been described previously (2,5,32). (B) Histogram showing the number of initial complexes (open bars) and the number of activator-dependent complexes surviving a 5 min heparin challenge (black bars).