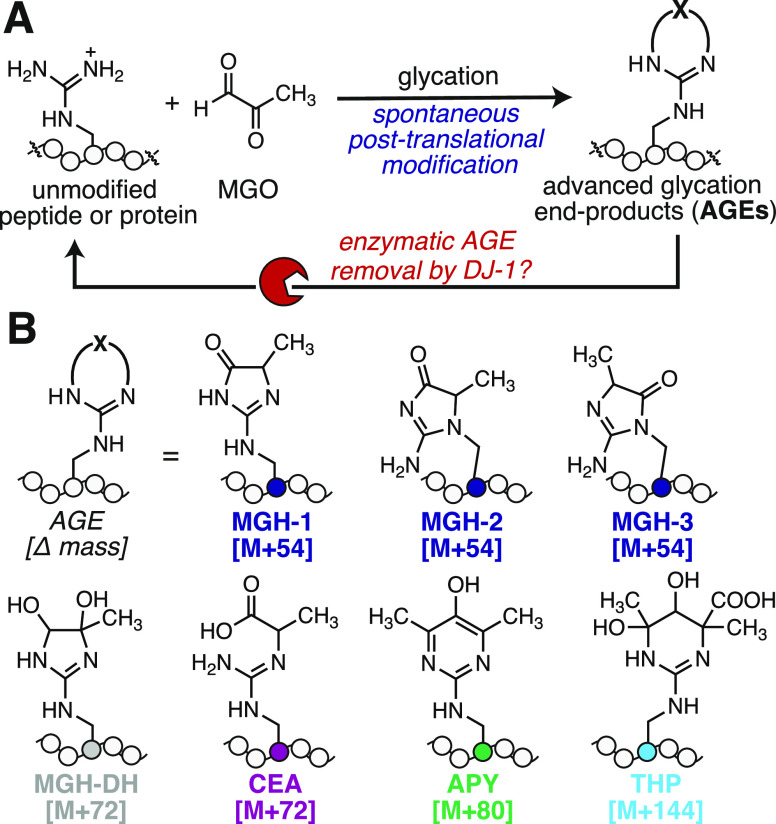
Figure 1.
DJ-1 is reported to be a glycation eraser. (A) Glycation is a nonenzymatic post-translational modification (PTM) that occurs preferentially at Arg or Lys residues. Unlike most PTMs, glycation occurs spontaneously and has no writer. There is significant interest in enzymes, like the Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1, that have the potential to erase glycation events. (B) Reaction of Arg with methylglyoxal (MGO), one of the most potent and prevalent cellular glycating agents, can produce numerous advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). These include the methylglyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone isomers (MGH-1, -2, -3), the dihydroxyimidazolidine (MGH-DH), carboxyethylarginine (CEA), argpyrimidine (APY), and tetrahydropyrimidine (THP).