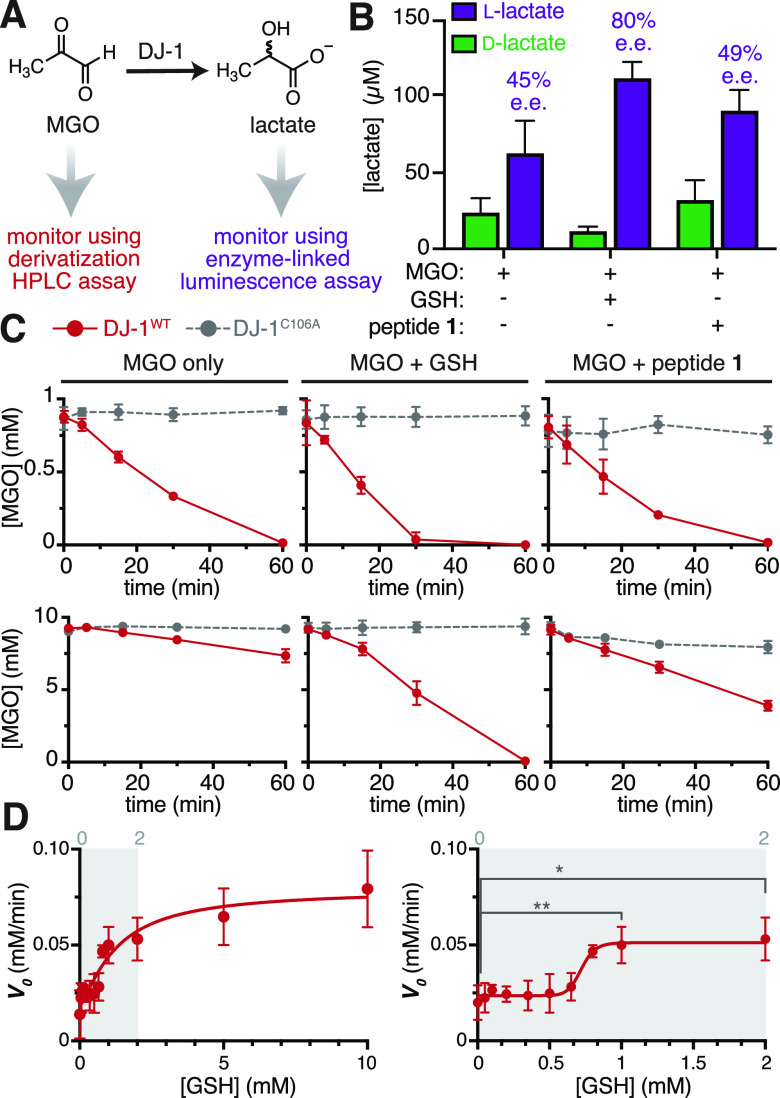
Figure 5.
DJ-1 is a glyoxalase that is allosterically activated by glutathione. (A) DJ-1 glyoxalase activity was measured in two ways: either by monitoring lactate production with a commercially available enzyme-linked luminescence assay or by monitoring the consumption of MGO in a quantitative HPLC chemical derivatization assay. (B) Using the luminescence assay, both d- and l-lactate were detected when 10 μM DJ-1WT was incubated for 30 min at 37 °C in 20 mM PBS at pH 7.3 with 1 mM MGO alone, 1 mM MGO and 1 mM GSH, or 1 mM MGO and 1 mM peptide 1. (C) Using the HPLC assay, time course studies were conducted using 100 μM DJ-1WT incubated with (top) 1 mM MGO, with or without equimolar GSH or peptide 1, or (bottom) 10 mM MGO, with or without equimolar GSH or peptide 1. Samples were incubated at 37 °C in 20 mM PBS at pH 7.3, and the resulting loss in MGO was monitored over 1 h. While DJ-1 exhibited modest differences in activity at low MGO (1 mM) concentrations, there was a major increase in activity when GSH was present at high (10 mM) MGO concentrations. (D) To evaluate if GSH could be an allosteric activator of DJ-1, we used the HPLC assay to monitor the reaction velocity (V0 = −d[MGO]/dt) over 30 min of treatment with 100 μM DJ-1WT and MGO (10 mM initial concentration), while titrating the GSH concentrations, up to 10 mM GSH (left). At low MGO concentrations (right), there was a sigmoidal relationship between GSH concentration and V0, suggesting that DJ-1 is allosterically activated by GSH. An unpaired Student’s t-test was used to determine statistically significant differences between V0 at 0 mM and either 1 mM or 2 mM GSH, p < 0.01(**), p < 0.05(*).