FIG 1.
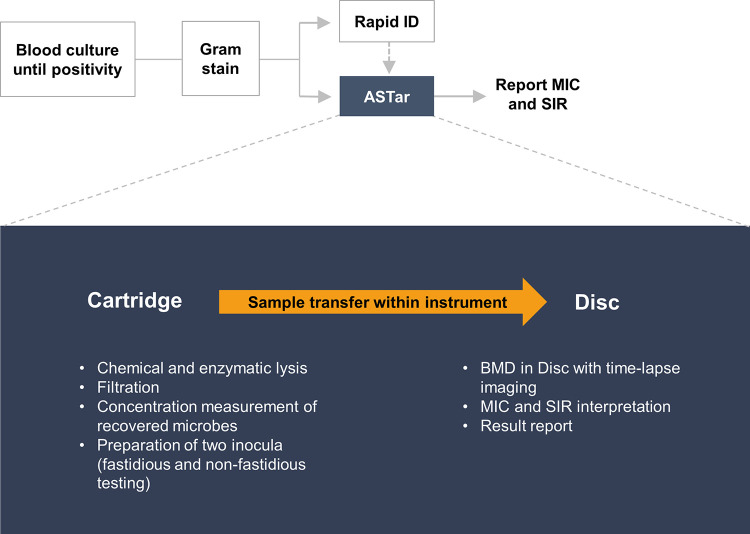
Example of the ASTar system’s clinical laboratory workflow. After blood culture positivity, Gram staining is performed. Next, a specimen can be loaded into the ASTar system for fully automated analysis (indicated in blue). In parallel, rapid identification (ID) can be performed with the laboratory’s standard methods. To start an ASTar run, a frozen insert should be placed into the cartridge along with a specimen from a Gram-negative, monomicrobial blood culture. The cartridge is scanned and loaded along with a disc into the instrument. The frozen insert contains all necessary reagents for the preparation of two inocula. Chemical and enzymatic lysis prepares the sample for filtration. The concentration of recovered microbes is then measured and adjusted to two inocula of 2 × 105 to 8 × 105 CFU/mL each. These are automatically pipetted onto the disc within the instrument, and BMD is performed on the disc, which contains antimicrobials at a range of 2-fold concentrations. Images from time-lapse microscopy are then analyzed with proprietary algorithms, and the MIC and category (SIR) are interpreted. The interpretation is dependent on species information, which should be provided at some point before results are reported.