Figure 2.
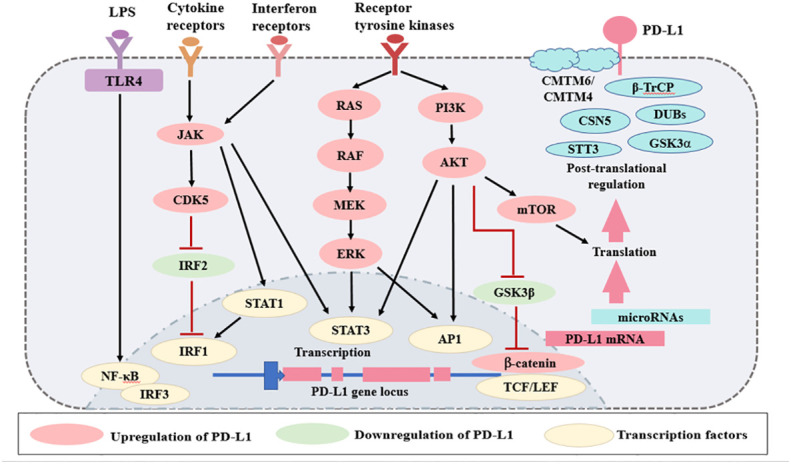
Regulation of PD-L1 expression. The expression of PD-L1 is regulated by several mechanisms. Various signaling pathways, such as TLRs, interferon receptors, cytokine receptors, and receptor tyrosine kinases, increase PD-L1 expression. There are several microRNAs that regulate PD-L1 mRNA transcription. Finally, PD-L1 is regulated at the protein level by protein circulation, ubiquitination, and glycosylation. Red lines represent inhibitory signals, and black lines represent stimulatory signals. AP1, activator protein 1; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; LEF, lymphoid enhancer- binding factor; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; NF- κB, nuclear factor κB; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; TCF, T cell- specific transcription factor; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; JAK, Janus kinase; CDK5, cyclin dependent kinase 5; CMTM, CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing; DUBs, deubiquitinating enzymes; STT3, subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex; GSK3α, glycogen synthase kinase 3α; β-TrCP, β-tranducin repeat-containing protein.
