FIGURE 3.
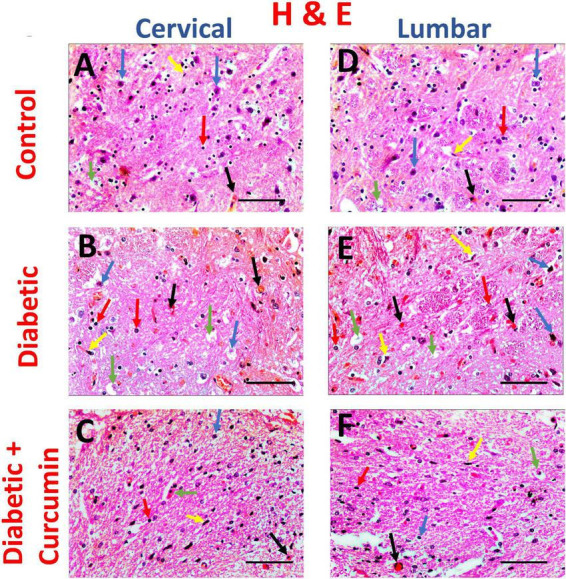
Impact of curcumin on histopathological changes in the dorsal horn of cervical and lumbar segments in diabetic rats by H & E (×400. Scale bar = 50 μm. The control group (A,D) revealed medium-sized basophilic somas of the sensory neurons (blue arrows) in acidophilic neutropil, myelinated axons with their myelin sheaths (green arrows), together with few glial cells; microglia (yellow arrows) and astrocytes (red arrows). Blood capillaries appear intervening (black arrows). The Diabetic group (B,E) revealed shrinkage of neuronal somas with surrounding haloes and pyknotic nuclei (blue arrows), degenerated axons (green arrows), multiple microglia (yellow arrows), and astrocytes (red arrows). Focal areas of hemorrhage (black arrows) are noticed. The Curcumin-treated group (C,F), revealed relatively normal neuronal somas, with few shrunken somas (blue arrows) in acidophilic neuropil. Relatively normal myelinated nerve axons, with few degenerated axons (green arrows), together with few glial cell nuclei; microglia (yellow arrows) and astrocytes (red arrows). Few areas of congestion (black arrows) are noticed.
