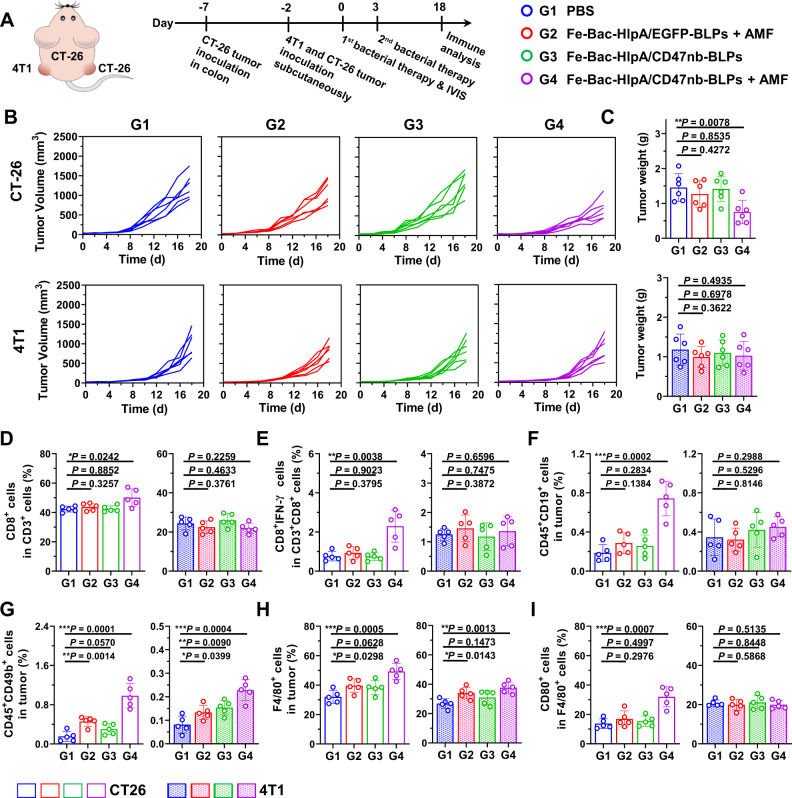
Fig. 8. Abscopal effect of the immunotherapy of AMF-Bac.
A Scheme and groups of in vivo therapy to evaluate the abscopal effect. BALB/c mice were inoculated with CT-26 cells in the colon on day -7, and subcutaneously inoculated with CT-26 and 4T1 cells in the right and left hind limb, respectively, on day -2. The mice were treated with engineered bacteria (1 × 108 CFU) by colon-specific administration on days 0 and 3, followed by AMF treatment (310 kHz and 23.8 kA/m) for 80 min at 24 h after colon administration. Tumors were collected for flow cytometry on day 18. B Change in tumor volume of the subcutaneous CT-26 and 4T1 xenografts (n = 5). C Tumor weight of the subcutaneous CT-26 and 4T1 xenografts measured on day 18 (n = 5 mice). D, E Flow cytometry analysis of the percentages of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in the total tumor-infiltrating CD3+ T cells (D), and effector CD8+ T cells (CD3+CD8+IFN-γ+ cells) in the total tumor-infiltrating CD3+CD8+ T cells (E) (n = 5 mice). F, G Flow cytometry analysis of the percentages of B cells (CD45+CD19+ cells; F) and NK cells (CD45+CD49b+ cells; G) in tumors (n = 5 mice). H, I Flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of macrophages (F4/80+ cells) in tumors (H), and the percentage of M1 macrophages (F4/80+CD80+ cells) in tumor-infiltrating macrophages (I; n = 5 mice). The data (C, D–I) are shown as the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by a two-tailed unpaired t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.