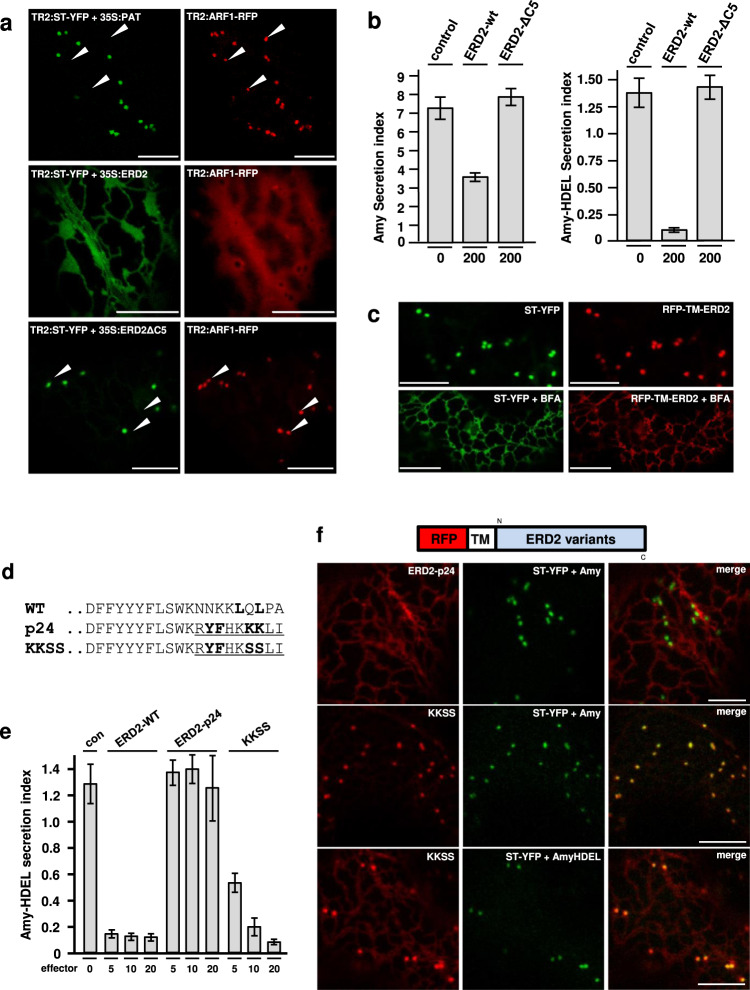
Fig. 5. A canonical COPI transport motif (KKXX) causes ER Localisation and abolishes Amy-HDEL retention of ERD2.
a C-terminal amino acid sequences of ERD2 wild type (WT) and two variants in which the last 9 amino acids of ERD2 is replaced by the corresponding region of p24 (underlined). The proposed COPII ER export signal of p24 (Contreras et al., 2004b) is in bold, as is the dileucine motif in the WT sequence, the relevant lysines of the canonical COPI transport motif in the p24 variant and finally the mutant serines in the KKSS variant. Size bars 10 microns. b Dose–response assay measuring the influence of co-transfected C-terminal ERD2 variants (given in standard GUS OD units below each lane) on Amy-HDEL secretion. ERD2-WT mediates strong cell retention whilst the p24 fusion shows no retention activity. The KKSS mutant of the p24 fusion restores the retention activity at the highest dose. Error bars are standard deviations from at least 4 biological replicas. c The effect of Brefeldin A on the transport of RFP-TM-ERD2 compared to ST-YFP. Notice that both fusions have re-distributed to the ER after 3 h of Brefeldin A treatment. Size bars 10 microns. d Sequence of the ERD2 C-terminus, the p24 fusion and the KKSS mutant thereof. e Amy-HDEL retention activity of constructs presented in (d). Fusing the p24 C-terminus renders ERD2 completely inactive, yet mutating the KKXX motif restores the bulk of biological activity. However, KKSS cannot meet the activity of the wild type ERD2 at lower doses. Error bars are standard deviations from at least 4 biological replicas. Source data are provided as a Source data file. f Localisation of p24 and KKSS hybrids incorporated into fluorescent ERD2 fusion proteins. The p24 C-terminus mediates complete ER localisation of the resulting ERD2 fusion whilst the KKSS mutant shows high steady-state levels at the Golgi. Size bars 10 microns.