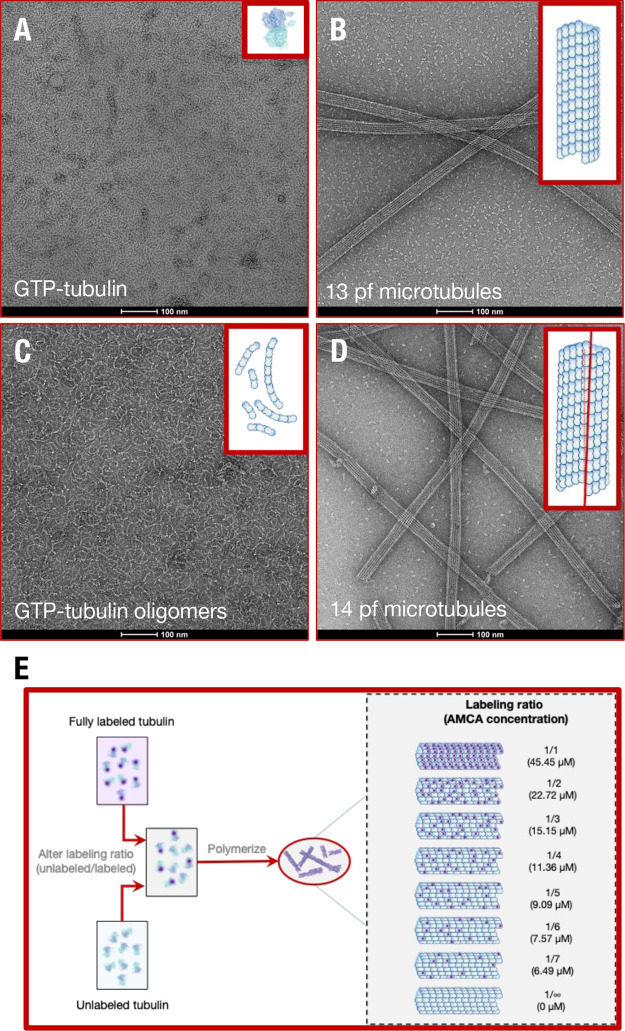
Figure 3.
Confirmation and polymerization of tubulin polymorphs. Negative stain electron microscopy of tubulin polymorphic geometries for (A) free GTP-tubulin in solution, (B) GTP-tubulin polymerized 13 protofilament microtubules, (C) free GTP-tubulin oligomers polymerized using 100 μM vinblastine in solution, and (D) GMPCPP-tubulin polymerized 14 protofilament microtubules. Insets show schematics of tubulin polymer structures. Methodology used to perform negative staining is described in SI Appendix. Due to MAPs and drugs that induce microtubule bundling being absent in our solutions and the highly charged C-termini tail of tubulin (expected to cause intermicrotubule repulsion), intermicrotubule separation distances were large enough in solution for electronic energy transfer to be insignificant. (E) Routine to polymerize microtubules with different AMCA labeled tubulin: unlabeled tubulin ratios, thus different AMCA concentrations. See SI Appendix for protocols used to assemble different tubulin polymerization states and perform electron microscopy.