Figure 4.
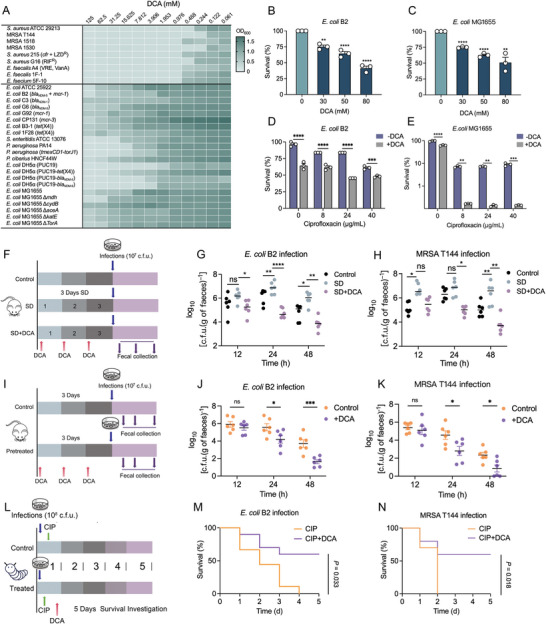
Antibacterial activity of DCA as well as its synergistic effect with existing antibiotics against bacterial infections. A) DCA sensitivity analysis in response to individual microbiota strains, including a panel of clinically drug‐resistant strains. Data represent the mean OD600 nm of three biological replicates. Dark green regions indicate higher cell density. B,C) Percent survival of B) E. coli B2 or C) E. coli MG1655 after exposure to increasing concentrations of DCA ranged from 0 × 10−3 to 80 × 10−3 m. D,E) DCA supplementation remarkably potentiates the bactericidal activity of CIP against D) multidrug‐resistant E. coli B2 and E) drug‐sensitive E. coli MG1655. F) Experimental protocols of DCA‐supplied intestinal infection model. The mice were randomly divided into three groups (n = 6 independent animals per group), including CON, SD, and SD + DCA groups. DCA administration, 100 mg kg−1 per day (i.p.). G,H) Bacterial loads in the feces of mice at 12, 24, and 48 h post‐infection by G) E. coli B2 or H) MRSA T144. I) Protocols of DCA‐pretreated administration in mice (n = 6 biologically independent animals per group). In the pretreated group, mice were supplied with a single intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of DCA (100 mg kg−1) for 3 consecutive days. J,K) Fecal colonization of invading pathogens in DCA‐pretreated mice infected by J) E. coli B2 or K) MRSA T144 (107 CFUs per mouse, i.g.). L) Protocol of the therapeutic potential assessment of combined use of DCA and CIP in vivo (n = 20 biologically independent larvae per group). M,N) Survival rate of Galleria mellonella larvae after 5 days postinfection by E. coli B2 or MRSA T144 (108 CFUs per larvae) and treated by CIP (10 × 10−6 m kg−1) alone or in combination with DCA (20 × 10−6 m kg−1). Data in (B)–(N) were displayed as mean ± SEM, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired t‐test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant). Experiments were performed with three biological replicates. Statistical significance in (J) and (K) was assessed by two‐way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison test.
