Figure 5.
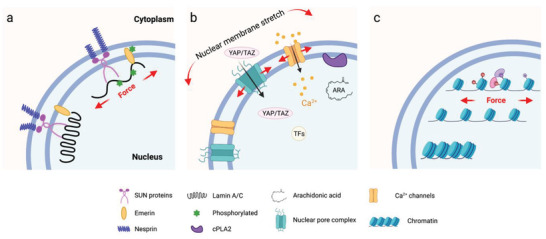
Nuclear membrane mechanotransduction. a) The nuclear envelope protein conformational changes responding to the exert force applied on the nucleus. b) Nuclear membrane stretch in response to force opens nuclear pore complexes, calcium channels, and activates cPLA2 on the cytoplasmic side, thus increasing calcium release, import of transcription factors (TFs), and production of arachidonic acid in the nucleoplasm. c) Mechanical forces applied to the nucleus may induce chromatin opening and epigenetic changes, that promote accessibility to TFs and regulate the downstream gene expression.
