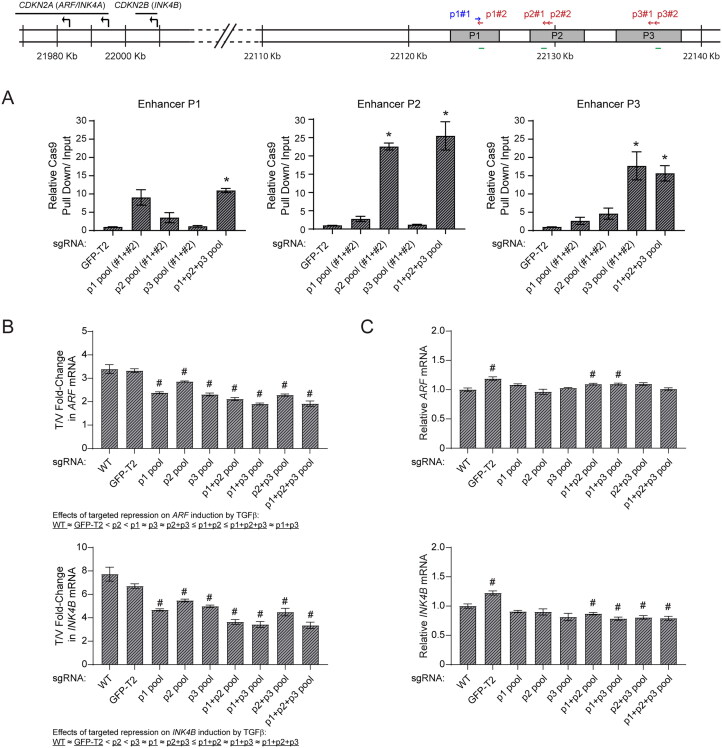
FIG 6.
Assessment of enhancer dependency within the TGFβ-dependent region on ARF/INK4B expression through CRISPRi in HeLa cells. (A) Quantitative analysis of representative ChIP assays by using anti-Cas9 antibodies to validate the recruitment of dCas9-KRAB to the previously defined enhancer peaks (P1, P2, and P3) located within TGFβ-dependent region. ChIP was performed using HeLa cells stably expressing dCas9-KRAB and sgRNAs targeting enhancer peaks either individually (P1, P2, and P3 pool) or concurrently (P1 + P2 + P3 pool), together with the one targeting GFP-T2 as a nontargeting control. The position of designed sgRNAs (arrows) in relation to enhancer peaks and genomic regions (green lines) where primers were designed to amplify immunoprecipitated DNA and input DNA are indicated in the schematic diagrams above. Pull down signal of the indicated locus is presented as relative pull down normalized against signal obtained in the “GFP-T2” group. (B-C) Quantitative analysis of mRNA expression of the indicated genes in HeLa cells with assigned enhancer peaks silenced through CRISPR interference, following vehicle or TGFβ treatment for 72 h. In the panel B, mRNA expression is presented as T/V fold-change with expression in TGFβ treated cells over one in vehicle treated cells, in comparison to the value obtained from control CRISPRi strains with either no sgRNA (WT) or nontargeting sgRNA (GFP-T2) expression. In the panel C, gene expression of the indicated genes are only shown with vehicle treated cells and normalized to the wild-type (WT) group, to address the effect of targeted enhancer silencing on baseline expression of the genes. Error bars: ±SEM. *P < 0.05, vs GFP-T2; #P < 0.05, vs WT.