Figure 2.1.
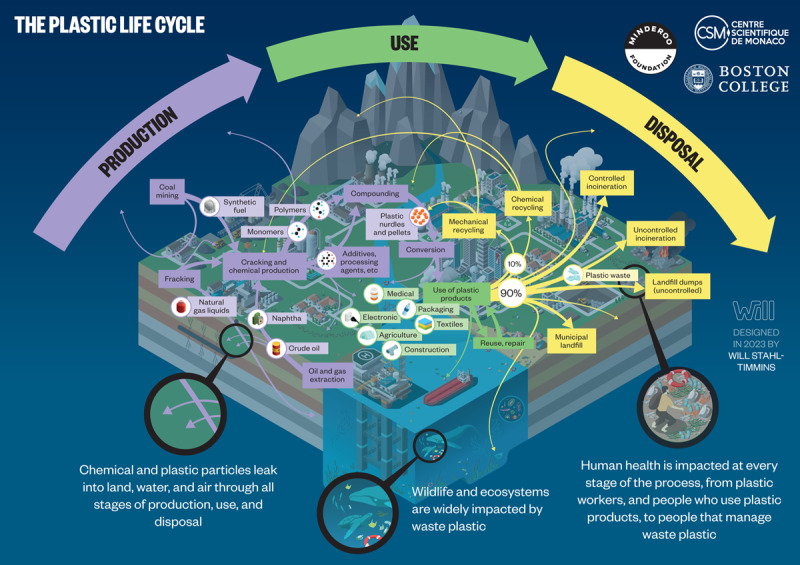
The plastic life cycle. The plastic life cycle is long and complex spanning multiple countries. There are three major phases. During production, carbon feedstocks – derived 99% from coal, oil and gas – are transformed through energy-intensive, catalytic processes into a vast array of products. Plastic is used in virtually every aspect of modern life and has provided many benefits. Single-use plastic constitutes the largest market share followed by synthetic fibers, building and construction, transport, electrical, agriculture and medical. Recycling is minimal. Disposal involves landfilling as well as controlled and uncontrolled burning. Plastic-laden e-waste is particularly problematic. Transnational environmental leakage of chemicals and plastic waste occurs throughout the life cycle resulting in extensive pollution and health hazards.
Credit: Designed in 2022 by Will Stahl-Timmins.
