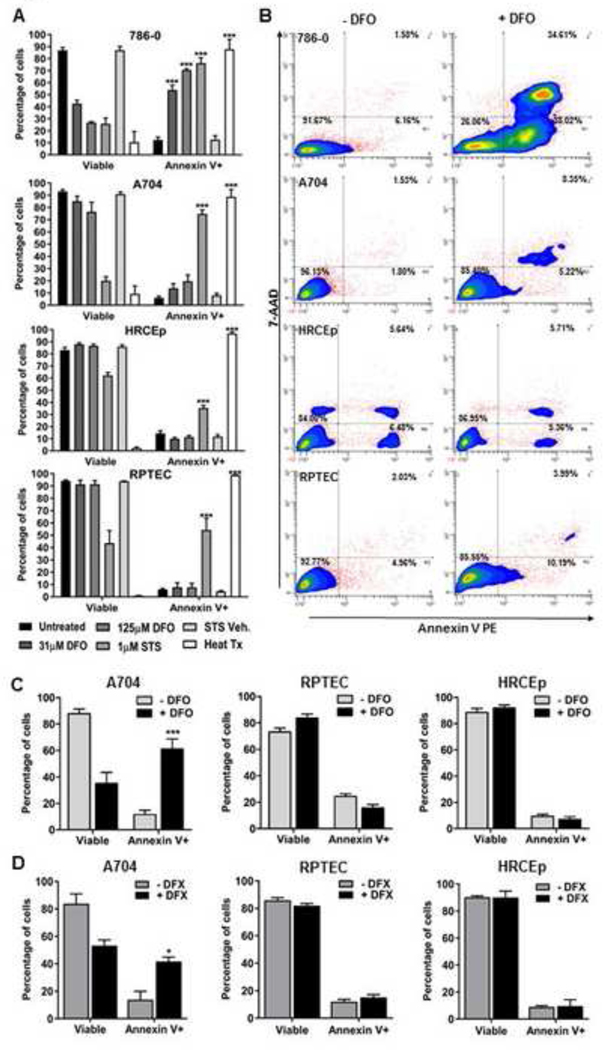
Figure 4. Iron chelation induces apoptosis in ccRCC cell lines but not benign renal cell lines.
Apoptosis was measured using Annexin V and 7AAD stain with flow cytometry in ccRCC (786–0 and A704) and benign renal (RPTEC and HRCEp) cell lines treated with 0, 31 or 125 μM DFO for 48 hours. Staurosporine (STS, 1 μM, 18 hours) drug was used as a positive control for apoptosis induction, in addition to its vehicle control, DMSO (STS Veh.). Heat-treated cells (Heat Tx) were used as a positive control for cell lysis and non-specific cell death. (A) Viable (7AAD(−)) and apoptotic (Annexin V(+)) cell percentages for ccRCC and benign renal cell lines are shown after treatment with and without DFO (31 or 125 μM) or control conditions. (B) Representative flow cytometry contour plots for 786–0, A704, HRCEp and RPTEC cells with and without DFO (125 μM) treatment. (C, D) Cell lines with resistance to apoptosis induction after 48-hour DFO treatment (A704, HRCEp and RPTEC) were subsequently treated with DFO for 120-hours (C), or DFX for 48 hours (D), and apoptosis was re-measured. All data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments, with error bars denoting SEM; *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 and ***, p<0.001 for comparison of treated and untreated cells using a two-tailed Student’s t-test.