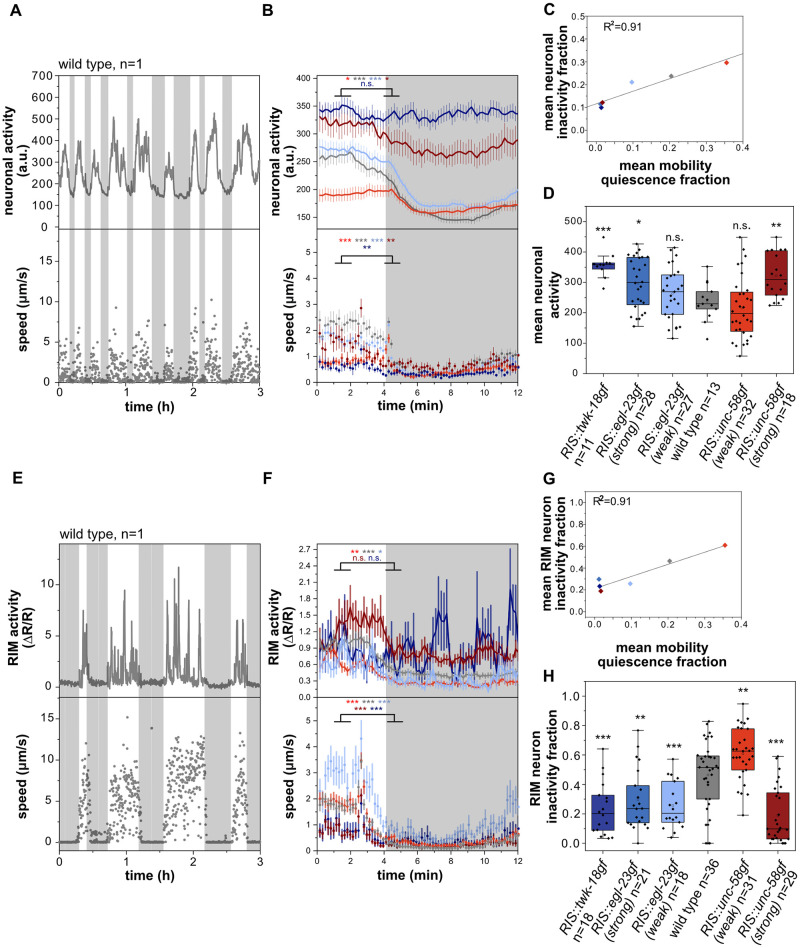
Fig 6. RIS::unc-58gf(strong) fails to inhibit wake-active circuits.
A-B) Reduced global neuronal activity (grey shading) correlates with motion quiescence (S1–S6 Movies). Head speed was measured. A) sample trace, B) alignment of overall neuronal activity to mobility quiescence bout onset. ***p<0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test. C) The mean neuronal inactivity fraction correlates with the mean mobility quiescence fraction (linear fit) for all strains. D) Strong RIS inactivation as well as RIS::unc-58gf(strong) caused an overall increase of neuronal activity. n.s. p > 0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p < 0.001, Welch test with FDR correction for multiple testing. E-F) RIM does not activate during mobility quiescence bouts. RIM speed was measured F) Sample trace (grey shade is RIM inactivity bout). Alignment of RIM activity and speed to mobility quiescence bout onset. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test. G) The mean RIM inactivity fraction correlates with the mean mobility quiescence fraction (linear fit) for all strains. H) Strong RIS inactivation as well as RIS::unc-58gf(strong) caused an overall increase of RIM activity. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Welch test with FDR correction for multiple testing.