Abstract
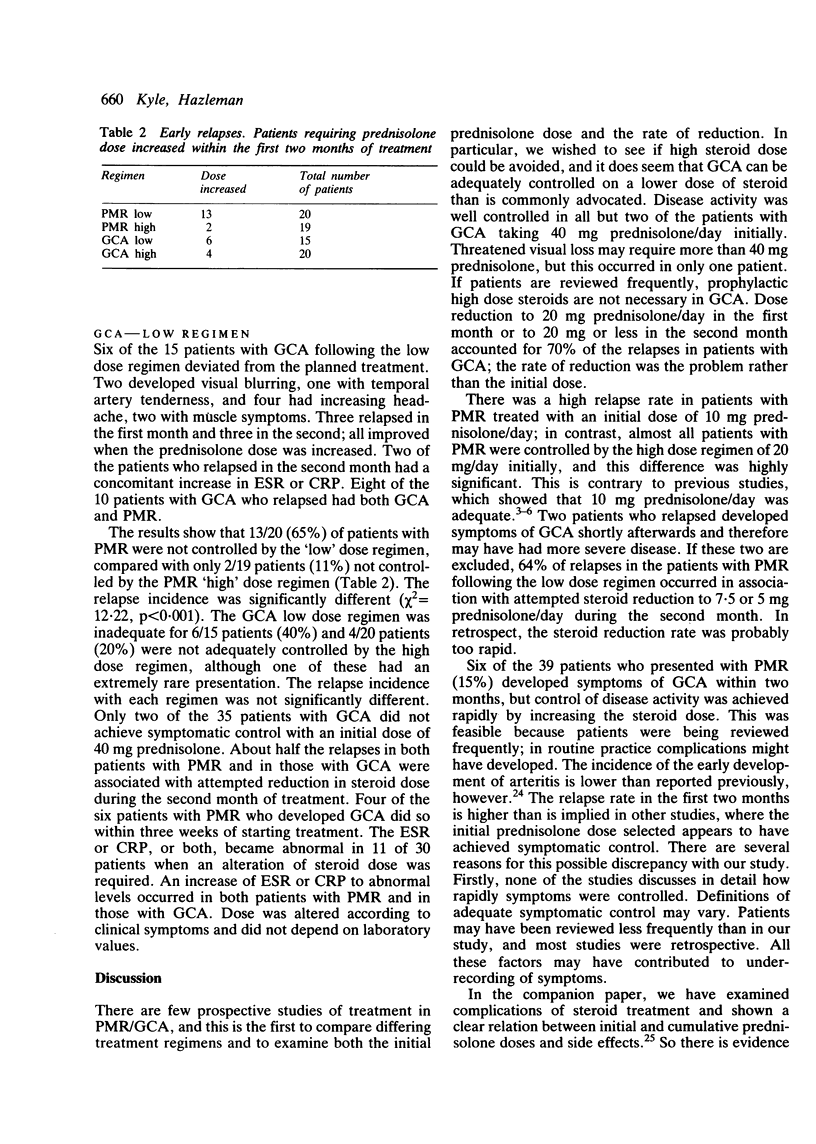
Thirty nine patients with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and 35 with giant cell arteritis (GCA) were treated with high or low dose steroid regimens in a prospective study of the first two months of treatment. Patients with PMR needed 15-20 mg prednisolone initially; 13/20 (65%) relapsed on an initial dose of 10 mg/day. All but two patients with GCA were successfully treated with 40 mg/day prednisolone initially but relapsed on a reduction to 20 mg/day. One patient with GCA receiving 30 mg/day relapsed after four weeks. Six patients with PMR developed GCA during the first two months and required an increased prednisolone dose to control symptoms. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C reactive protein did not predict relapse.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayoub W. T., Franklin C. M., Torretti D. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Duration of therapy and long-term outcome. Am J Med. 1985 Sep;79(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behn A. R., Perera T., Myles A. B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and corticosteroids: how much for how long? Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Aug;42(4):374–378. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. A., Malmvall B. E. Prognosis of giant cell arteritis including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. A follow-up study on ninety patients treated with corticosteroids. Acta Med Scand. 1981;209(5):337–345. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1981.tb11604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. Y., Hunder G. G., Ilstrup D. M., Kurland L. T. Polymyalgia rheumatica: a 10-year epidemiologic and clinical study. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Nov;97(5):672–680. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-5-672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. B., Hurd E. R. Neurological complications of connective tissue and other "collagen-vascular" diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Aug;11(1):190–212. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(81)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esselinckx W., Doherty S. M., Dixon A. S. Polymyalgia rheumatica. Abrupt and gradual withdrawal of prednisolone treatment, clinical and laboratory observations. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):219–224. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald P., Rygvold O., Oystese B. Temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Clinical and biopsy findings. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Dec;77(6):845–852. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-6-845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. W., Jr Temporal arteritis. Am J Med. 1979 Nov;67(5):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90744-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham E., Holland A., Avery A., Russell R. W. Prognosis in giant-cell arteritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jan 24;282(6260):269–271. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6260.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. R., Jr, Shelley W. M., Tumulty P. A. Giant cell arteritis: including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Jan;50(1):1–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubault A. La pseudo-polyarthrite rhizomélique. Presse Med. 1983 Jan 22;12(3):157–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston K. A., Hunder G. G. Giant cell (cranial) arteritis: a clinical review. Am Heart J. 1980 Jul;100(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson F., Cullen J. F., Elton R. A. Temporal arteritis. A 14-year epidemiological, clinical and prognostic study. Scott Med J. 1979 Apr;24(2):111–117. doi: 10.1177/003693307902400203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. G., Hazleman B. L. Prognosis and management of polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Feb;40(1):1–5. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogstad O. A. Polymyalgia rheumatica and its relation to arteritis temporalis. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Nov;178(5):591–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle V., Hazleman B. L. Treatment of polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. II. Relation between steroid dose and steroid associated side effects. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Aug;48(8):662–666. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.8.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myles A. B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a seven-year survey. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1975 Nov;14(4):231–235. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/14.4.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen S., Lorenzen I. Giant-cell arteritis, temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. A retrospective study of 63 patients. Acta Med Scand. 1977;201(3):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb15683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiera H., Davison S. Long-term follow-up of polymyalgia rheumatica. Mt Sinai J Med. 1978 Mar-Apr;45(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD A. G., BATEMAN M., COOKE W. T. TEMPORAL ARTERITIS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1963 Sep;47:555–566. doi: 10.1136/bjo.47.9.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadman B., Werner I. Observations on temporal arteritis. Acta Med Scand. 1972 Nov;192(5):377–383. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb04833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


